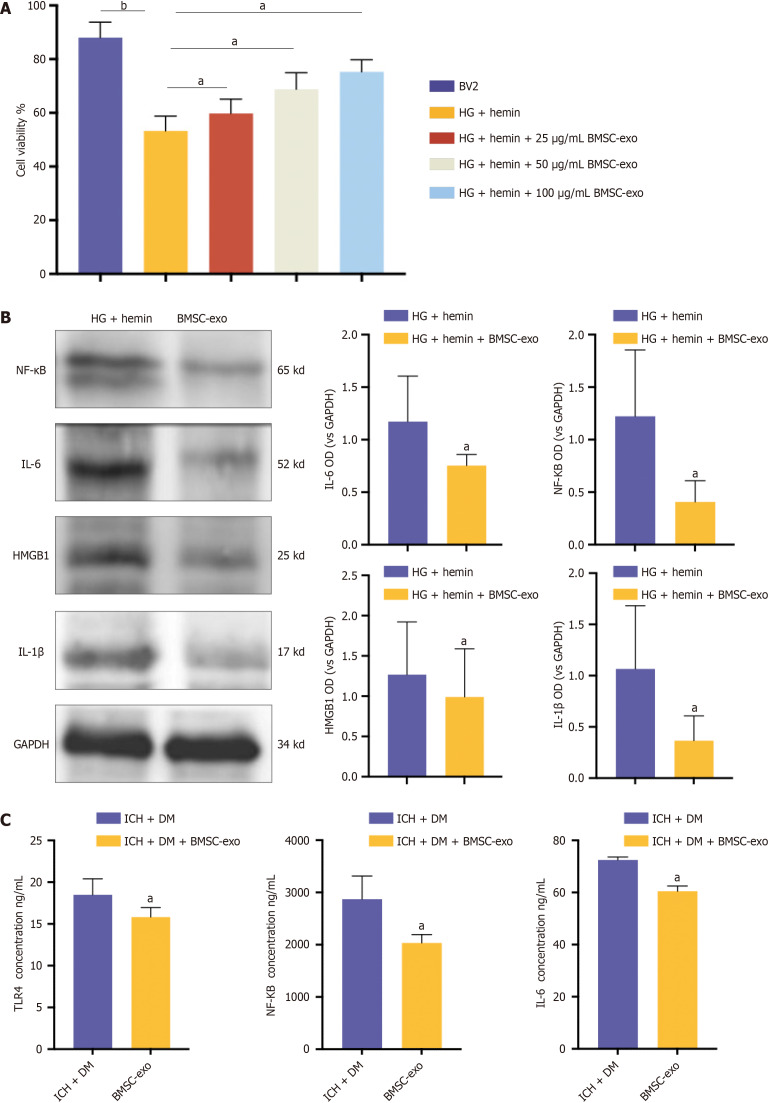
Figure 4.
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome attenuated neuroinflammation in mice with diabetes and intracerebral hemorrhage. A: Microglia were treated with different concentrations of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (BMSC-exo), and cell viability was observed using the cell counting kit-8 assay. Experimental data are expressed as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, BV2 group vs high glucose (HG) + hemin group; aP < 0.05, HG + hemin group vs HG + hemin + 25 μg/mL BMSC-exo group; aP < 0.05, HG + hemin group vs HG + hemin + 50 μg/mL BMSC-exo group; aP < 0.05, HG + hemin group vs HG + hemin + 100 μg/mL BMSC-exo group, t-test; B: Western blot assay was performed to detect the expression levels of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), interleukin (IL) 6, IL-1β, and high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) inflammatory factors in the cells. Experimental data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, HG + hemin group vs HG + hemin + BMSC-exo group, t-test; C: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detection of toll-like receptor 4, NF-κB, and IL-6 expression. Experimental data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) + diabetes mellitus (DM) group vs ICH + DM + BMSC-exo group, t-test. BMSC-exo: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes; HG: High glucose; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; IL: Interleukin; HMGB1: High-mobility group box 1; TLR: Toll-like receptor; DM: Diabetes mellitus; ICH: Intracerebral hemorrhage.