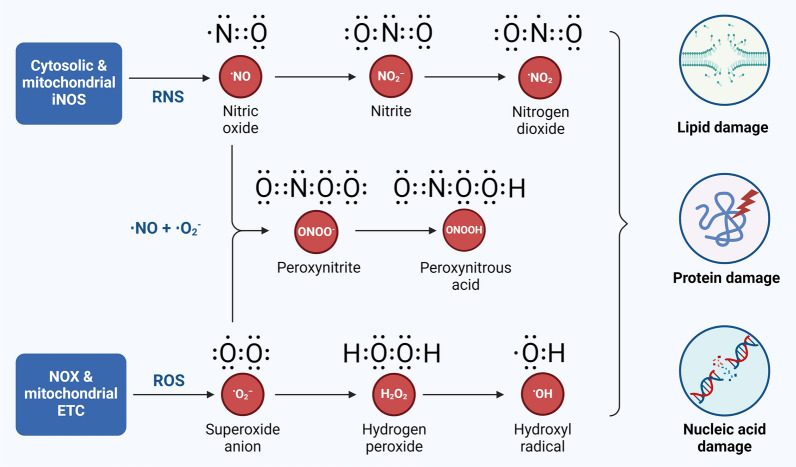
Fig. 1.
Pathways of RNS and ROS production in sepsis. Excessive nitric oxide is generated by both cytosolic and mitochondrial iNOS during sepsis. The nitric oxide can be converted to other reactive nitrogen species (RNS), such as nitrite and nitrogen dioxide. On the other hand, excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced by NOXs and mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC). Nitric oxide and superoxide react to form additional derivatives, notably the highly toxic peroxynitrite. The accumulation of these reactive species inflicts damage to cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, thereby compromising mitochondrial respiration and integrity