Fig. 2.
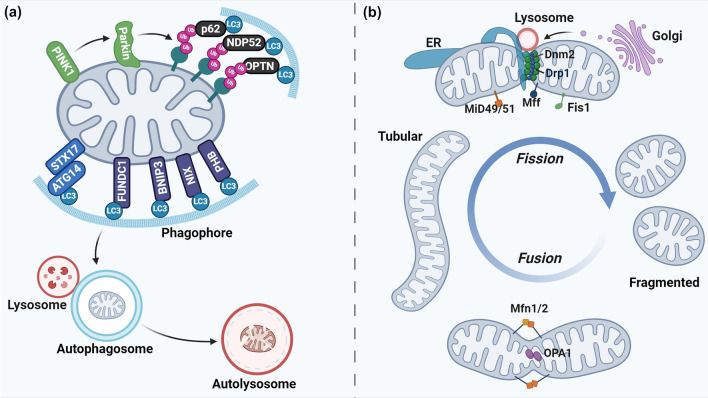
Pathways of mitophagy and mitochondrial dynamics. a The most extensively studied mitophagy pathway involves PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin. Upon ΔΨm loss, PINK1 is stabilized on the OMM, where it recruits and activates Parkin. Parkin subsequently ubiquitinates mitochondrial surface proteins, signaling the autophagosome to encapsulate the dysfunctional mitochondrion. Adaptor proteins including p62, Optineurin (OPTN), calcium binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 2 (NDP52), tax1-binding protein 1 (TAX1BP1), and next to BRCA1 gene 1 protein (NBR1) play a role in linking the ubiquitin chains to microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) on phagophores. On the other hand, some mitochondrial receptor proteins (or lipids) such as FUN14 domain containing 1 (FUNDC1), prohibitin (PHB), BCL2 interacting protein3 (BNIP3), Nip3-like protein X (NIX), cardiolipin, and syntaxin 17 (STX17) can recruit phagophore membranes independent of ubiquitin. The autophagosome finally fuses with a lysosome for the degradation and recycling of mitochondria. b Mitochondrial dynamics is regulated by several dynamin-related GTPases, including Mfn1/2, OPA1, Drp1, Fis1, MiD49/51, and Mff. Mfn1/2 facilitate the fusion of the OMM, while OPA1 is responsible for the fusion of the IMM. The fission process is initiated by the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mediated pre-constriction of mitochondria. Drp1 is recruited to the pre-constricted sites by receptors (Mff, Fis1, and MiD49/51). After binding to OMM, Drp1 oligomerizes into ring-shaped filaments. Hydrolysis of GTP by Drp1 results in constriction and closure of the ring. Dnm2 is finally recruited to the constricting site to complete the fission. In addition to the ER, lysosome and Golgi-derived vesicles have also been reported to regulate mitochondrial fission