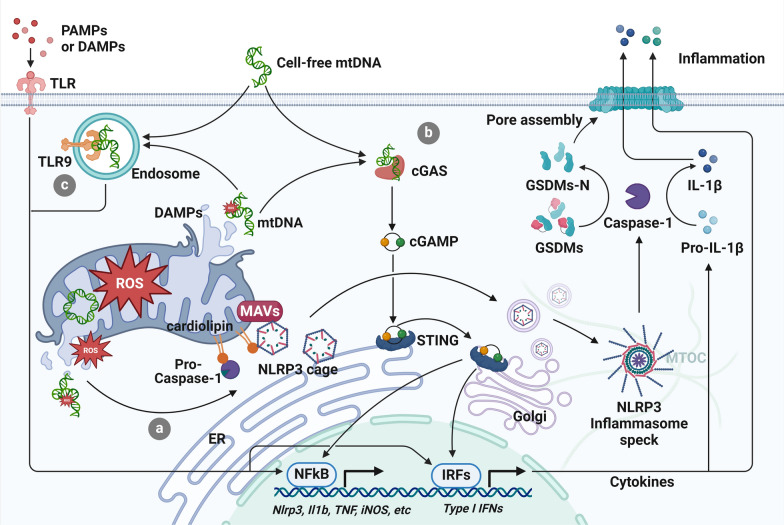
Fig. 4.
Mitochondria-regulated inflammatory pathways in sepsis. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) of immune cells recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) from microbes or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) released by damaged host cells. a Mitochondria orchestrate the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. mtROS and ox-mtDNA promote the NLRP3 inflammasome activation after their release from the damaged mitochondria. Additionally, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) and cardiolipin mediate the spatial association between mitochondria and NLRP3, which may facilitate a rapid and efficient sensing of the inflammatory signals from the damaged mitochondria by NLRP3. Early studies posited mitochondria or mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM) as the docking sites of NLRP3, while more recent publications have indicated the involvement of Golgi and microtubule-organizing center (MTOC). It could be plausible that NLRP3 proteins are first transported to meet mitochondria, after which NLRP3 redistributes to the adjacent Golgi apparatus as oligomeric cages. Then, the NLRP3 cages are transported to MTOC and reorganized into a single inflammasome speck. Activated NLRP3 inflammasome mediates the activation of pro-caspase-1, which proteolytically processes GSDMs and pro-inflammatory cytokines. The matured cytokines are released from the GSDMs pores to transmit inflammatory signals. b Mitochondria regulate the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway. cGAS is activated upon mtDNA binding, leading to the synthesis of cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP). cGAMP then induces a conformational change in STING, leading to its activation at ER. Activated STING translocates to Golgi, where it activates transcription factors interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) to initiate the production of type I interferons and other pro-inflammatory cytokines that are required for effective immune response against pathogens. c Mitochondria regulate the TLR9 pathway. mtDNA shares similarities with bacterial DNA, thus can be recognized by TLR9. As with other TLRs and cGAS-STING axis, TLR9 pathway activates IRF3 and NF-κB to regulate the inflammatory response