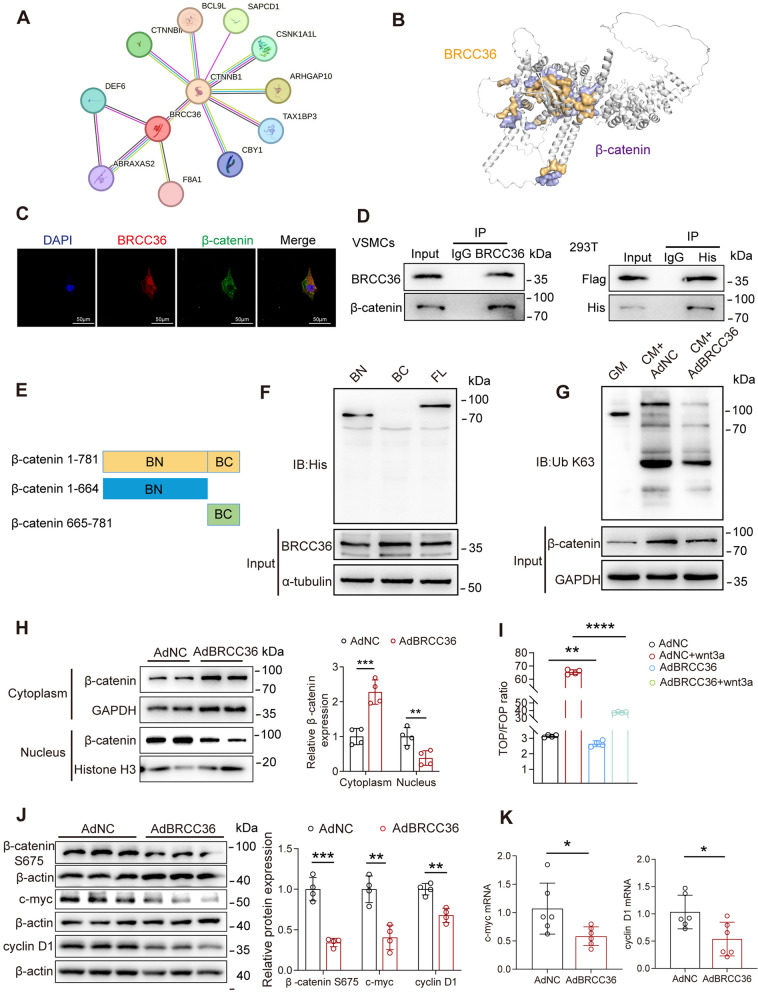
Fig. 5.
BRCC36 suppresses β-catenin nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity by inhibiting K63-linked β-catenin polyubiquitination. A Predicted BRCC36-β-catenin interaction was done by STRING database. B Molecular docking assays of BRCC36 and β-catenin. C The co-localization of BRCC36 and β-catenin in VSMCs was detected by double-labeling immunofluorescence. Scale bar, 50 μm. D BRCC36 interaction with β-catenin in VSMCs and exogenous interaction of BRCC36 and β-catenin in HEK293T cells was detected by Co-IP. E A diagram showing the plasmid construct containing different domains of β-catenin. F The exact domain of β-catenin interacts with BRCC36 was determined by Co-IP. G The K63 ubiquitination alterations of β-catenin were detected by western blotting after BRCC36 overexpression. H Detection of β-catenin localization by nucleocytoplasmic separation experiments after BRCC36 overexpression. I The activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was detected by TOP/FOPFlash assay. J VSMCs were transfected with Ad-vector or Ad-BRCC36. Western blot analysis of protein levels of β-catenin S675, c-myc, cyclinD1, and β-actin. K RT-qPCR analysis of the mRNA levels of c-myc and cyclin D1, n = 6 per group. Statistical significance was assessed using two tailed t-test (H, I, J, K). All values are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05