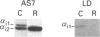Abstract
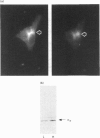
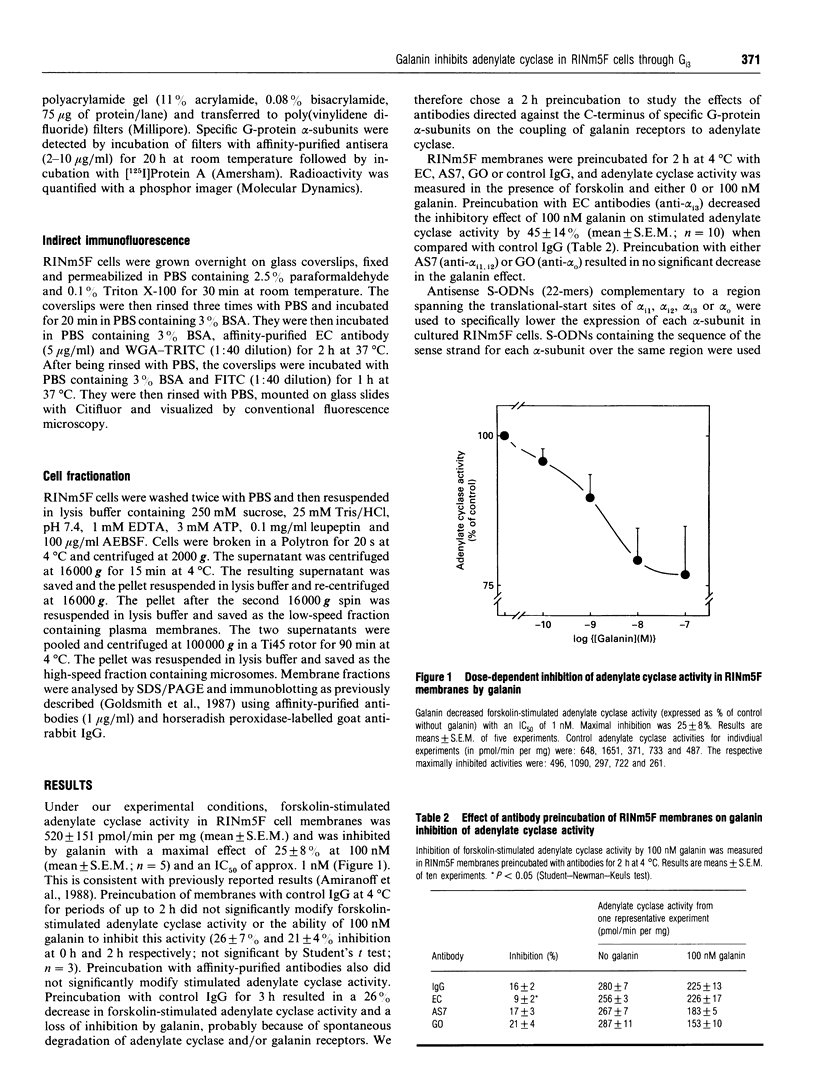
Galanin inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and insulin secretion and modulates ion channels in pancreatic beta-cells through pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-protein(s). Antibodies directed against the C-terminal region of specific G-protein alpha-subunits were used to determine which G-protein(s) couple galanin receptors to inhibition of adenylate cyclase in the rat insulinoma cell line RINm5F. Preincubation of membranes with EC antibody (anti-alpha i3) decreased the inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity by galanin (100 nM) by 45% compared with control IgG (P < 0.05) whereas preincubation with AS (anti-alpha i1, alpha i2) or GO (anti-alpha o) antibodies had no significant effect. To confirm these results, RINm5F cells were exposed intermittently over a 4-day period to phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides that were either sense or antisense to alpha i1, alpha i2, alpha i3 or alpha o. Oligodeoxynucleotides antisense to alpha i2, alpha i3 and alpha o specifically decreased the levels of the targeted alpha-subunit in membranes. alpha i1 was undetectable in these cells. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity by galanin was largely abolished in membranes from cells exposed to the oligodeoxynucleotide antisense to alpha i3, whereas all other oligodeoxynucleotides had no significant effect on this pathway. Indirect immunofluorescence and immunoblotting of specific membrane fractions with EC antibody show significant localization of alpha i3 to intracellular membrane compartments. These results suggest that Gi3 is the G protein that couples galanin receptors to inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in RINm5F cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrén B., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Galanin and the endocrine pancreas. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Gautam N., Fong H. K., Northup J. K., Simon M. I. The 35- and 36-kDa beta subunits of GTP-binding regulatory proteins are products of separate genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5008–5011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Laburthe M. Galanin receptor in the rat pancreatic beta cell line Rin m 5F. Molecular characterization by chemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20714–20717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Lagny-Pourmir I., Laburthe M. Mechanism of galanin-inhibited insulin release. Occurrence of a pertussis-toxin-sensitive inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aridor M., Rajmilevich G., Beaven M. A., Sagi-Eisenberg R. Activation of exocytosis by the heterotrimeric G protein Gi3. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1569–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.7504324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Reisine T. Molecular biology of somatostatin receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Jan;16(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90050-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormont M., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Van Obberghen E., Spiegel A. M., Sharp G. W. Identification of G protein alpha-subunits in RINm5F cells and their selective interaction with galanin receptor. Diabetes. 1991 Sep;40(9):1170–1176. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.9.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Bullett M. J., Li G. D., Wollheim C. B., Petersen O. H. Galanin activates nucleotide-dependent K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):413–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargin A., Yamamoto K., Cotecchia S., Goldsmith P. K., Spiegel A. M., Lapetina E. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Dual coupling of the cloned 5-HT1A receptor to both adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase C is mediated via the same Gi protein. Cell Signal. 1991;3(6):547–557. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90031-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermouet S., de Mazancourt P., Spiegel A. M., Farquhar M. G., Wilson B. S. High level expression of transfected G protein alpha i3 subunit is required for plasma membrane targeting and adenylyl cyclase inhibition in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 9;312(2-3):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80940-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homaidan F. R., Sharp G. W., Nowak L. M. Galanin inhibits a dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ current in the RINm5f cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8744–8748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Toyama R., Kozasa T., Tsukamoto T., Matsuoka M., Kaziro Y. Presence of three distinct molecular species of Gi protein alpha subunit. Structure of rat cDNAs and human genomic DNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6656–6664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Perfusion of the pancreas isolated from pertussis-sensitized rats: potentiation of insulin secretory responses due to beta-adrenergic stimulation. Endocrinology. 1977 Oct;101(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-4-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Different beta-subunits determine G-protein interaction with transmembrane receptors. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):424–426. doi: 10.1038/358424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):832–834. doi: 10.1126/science.8094261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagny-Pourmir I., Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Tatemoto K., Laburthe M. Characterization of galanin receptors in the insulin-secreting cell line Rin m 5F: evidence for coupling with a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanosine triphosphate regulatory protein. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2635–2641. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. F., Yasuda K., Bell G. I., Reisine T. Gi alpha 3 and G(o) alpha selectively associate with the cloned somatostatin receptor subtype SSTR2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10721–10727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis M. J., Bourne H. R. Activation of the alpha subunit of Gs in intact cells alters its abundance, rate of degradation, and membrane avidity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1297–1307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyte A., Barr F. A., Kehlenbach R. H., Huttner W. B. Multiple trimeric G-proteins on the trans-Golgi network exert stimulatory and inhibitory effects on secretory vesicle formation. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4795–4804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClue S. J., Selzer E., Freissmuth M., Milligan G. Gi3 does not contribute to the inhibition of adenylate cyclase when stimulation of an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor causes activation of both Gi2 and Gi3. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):565–568. doi: 10.1042/bj2840565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean I., Mullaney I., Brown D. A., Milligan G. Antibodies to the GTP binding protein, Go, antagonize noradrenaline-induced calcium current inhibition in NG108-15 hybrid cells. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. M., Hod Y., Malbon C. C. Induction of G alpha i2-specific antisense RNA in vivo inhibits neonatal growth. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):991–995. doi: 10.1126/science.8493537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pobiner B. F., Northup J. K., Bauer P. H., Fraser E. D., Garrison J. C. Inhibitory GTP-binding regulatory protein Gi3 can couple angiotensin II receptors to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):156–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Seaquist E. R., Walseth T. F. G proteins and modulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):1–6. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hescheler J., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Hinsch K. D., Klinz F. J., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Gausepohl H., Frank R. Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins in the hormonal inhibition of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ currents in an insulin-secreting cell line (RINm5F). J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18025–18033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Yada T., Russo L. L., Bliss C. R., Cormont M., Monge L., Van Obberghen E. Galanin can inhibit insulin release by a mechanism other than membrane hyperpolarization or inhibition of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7302–7309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker A., Goldsmith P., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. The G protein coupled to the thromboxane A2 receptor in human platelets is a member of the novel Gq family. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9309–9313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbert S., Michel T., Lee R., Neer E. J. Differential degradation rates of the G protein alpha o in cultured cardiac and pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3102–3105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Woodard C. J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Receptor and effector interactions of Gs. Functional studies with antibodies to the alpha s carboxyl-terminal decapeptide. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80622-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M., Shenker A., Weinstein L. S. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins: implications for normal and abnormal signal transduction. Endocr Rev. 1992 Aug;13(3):536–565. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-3-536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow J. L., de Almeida J. B., Narula N., Holtzman E. J., Ercolani L., Ausiello D. A. A heterotrimeric G protein, G alpha i-3, on Golgi membranes regulates the secretion of a heparan sulfate proteoglycan in LLC-PK1 epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1113–1124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallent M., Reisine T. Gi alpha 1 selectively couples somatostatin receptors to adenylyl cyclase in pituitary-derived AtT-20 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):452–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylyl cyclases. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):869–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1500–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.1962211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by Gi alpha. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.8327893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Toyama R., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Matsuoka M., Kaziro Y. Structure of the human gene and two rat cDNAs encoding the alpha chain of GTP-binding regulatory protein Go: two different mRNAs are generated by alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B. Galanin inhibits insulin secretion by direct interference with exocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):401–404. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81379-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. Y., Watkins D. C., Malbon C. C. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to GS protein alpha-subunit sequence accelerate differentiation of fibroblasts to adipocytes. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):334–337. doi: 10.1038/358334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. C., Johnson G. L., Malbon C. C. Regulation of the differentiation of teratocarcinoma cells into primitive endoderm by G alpha i2. Science. 1992 Nov 20;258(5086):1373–1375. doi: 10.1126/science.1455234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Gilbert D. J., Olsen A. S., Chen X. N., Amatruda T. T., Korenberg J. R., Trask B. J., de Jong P., Reed R. R., Simon M. I. Evolution of the mammalian G protein alpha subunit multigene family. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):85–91. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Komuro M., Farquhar M. G. Cellular variations in heterotrimeric G protein localization and expression in rat pituitary. Endocrinology. 1994 Jan;134(1):233–244. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.1.8275939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. H., Conklin B. R., Bourne H. R. Gz-mediated hormonal inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):339–342. doi: 10.1126/science.1347957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida J. B., Holtzman E. J., Peters P., Ercolani L., Ausiello D. A., Stow J. L. Targeting of chimeric G alpha i proteins to specific membrane domains. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):507–515. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels that are blocked by hypoglycemia-inducing sulfonylureas in insulin-secreting cells are activated by galanin, a hyperglycemia-inducing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1312–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]