Abstract
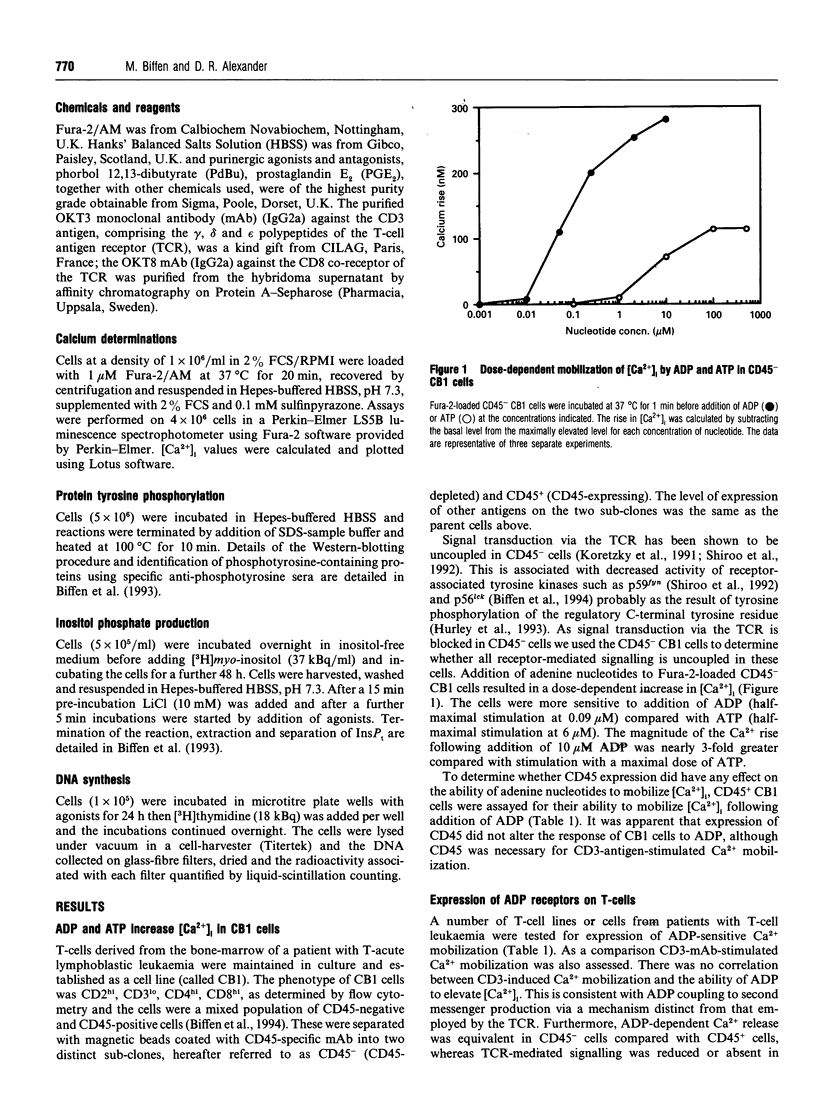
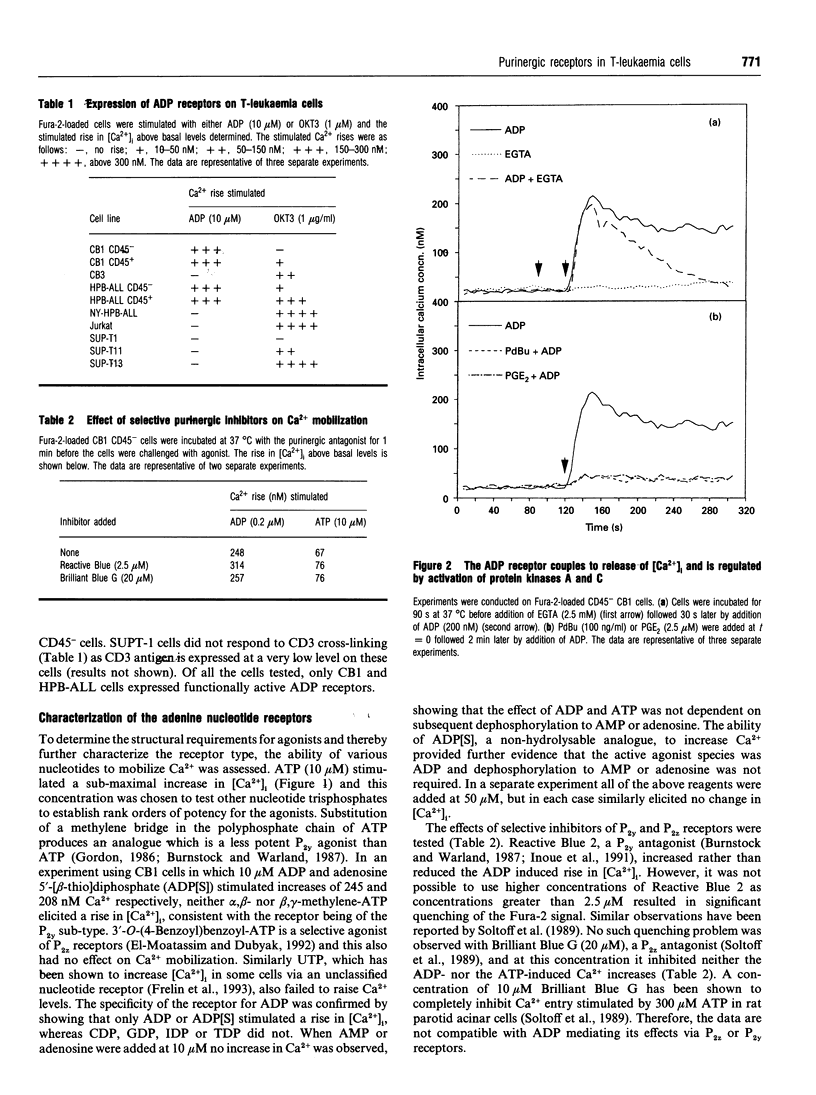
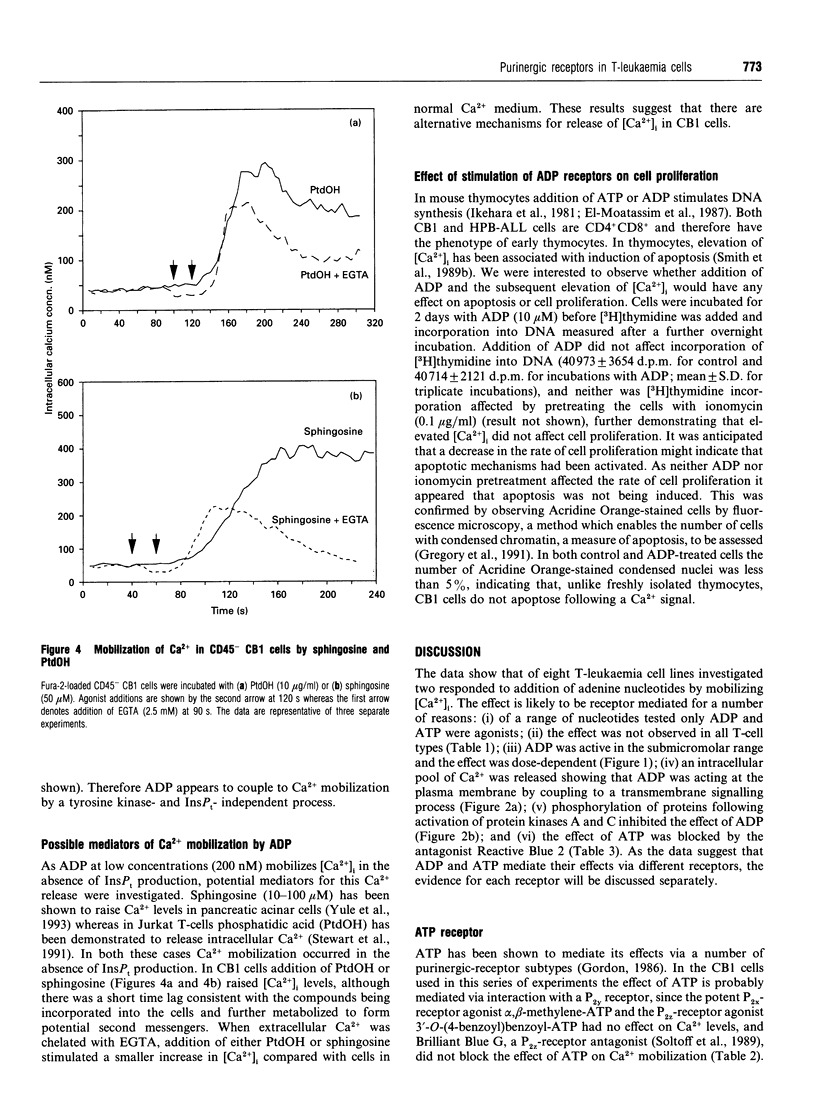
The expression of purinergic receptors on human T-cells was investigated and the receptors were shown to be functionally coupled to intracellular signals in two out of eight T-leukaemia cell-lines. Addition of adenine nucleotides resulted in mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in HPB-ALL cells and a cell line (CB1) recently isolated from a patient with T-acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Of a range of nucleotides tested only ADP and ATP elevated intracellular levels of Ca2+, with ADP being the more potent agonist. Ca2+ mobilization by ATP was accompanied by increased inositol phosphate production and was blocked by the purinergic receptor antagonist, Reactive Blue 2, indicating that ATP was interacting with a P2y receptor. Intracellular Ca2+ release triggered by ADP was independent of both inositol phosphate production and protein tyrosine phosphorylation. Expression of the transmembrane phosphotyrosine phosphatase, CD45, had no effect on ADP-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization. Our results show that functional P2y receptors can be expressed on T-cells, and also identify a novel T-cell ADP receptor. Signals mediated by these purinergic receptors could play important roles in modulating T-cell function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biffen M., McMichael-Phillips D., Larson T., Venkitaraman A., Alexander D. The CD45 tyrosine phosphatase regulates specific pools of antigen receptor-associated p59fyn and CD4-associated p56lck tyrosine in human T-cells. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1920–1929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biffen M., Shiroo M., Alexander D. R. G-proteins are not directly involved in the CD3-antigen-mediated production of inositol phosphates in HPB-ALL T-leukaemia cells expressing phospholipase C isoforms gamma 1 and beta 3. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 15;289(Pt 2):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2890387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Warland J. J. P2-purinoceptors of two subtypes in the rabbit mesenteric artery: reactive blue 2 selectively inhibits responses mediated via the P2y-but not the P2x-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;90(2):383–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher G. J., Bakshian S., Baldassare J. J. Activation of human platelets by ADP causes a rapid rise in cytosolic free calcium without hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):958–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91984-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman R. F., Rubin A. L., Novogrodsky A., Stenzel K. H. Selective suppression of blastogenesis induced by different mitogens: effect of noncyclic adenosine-containing compounds. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 15;54(1):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Breittmayer J. P., Vigne P. ADP induces inositol phosphate-independent intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in brain capillary endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8787–8792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Dive C., Henderson S., Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Gordon J., Rickinson A. B. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes protects human B cells from death by apoptosis. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):612–614. doi: 10.1038/349612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holter W., Spiegel A. M., Howard B. H., Weber S., Brann M. R. Expression of GTP-binding proteins and prostaglandin E2 receptors during human T cell activation. Cell Immunol. 1991 May;134(2):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90303-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. R., Hyman R., Sefton B. M. Differential effects of expression of the CD45 tyrosine protein phosphatase on the tyrosine phosphorylation of the lck, fyn, and c-src tyrosine protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1651–1656. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara S., Pahwa R. N., Lunzer D. G., Good R. A., Modak M. J. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate-(ATP) mediated stimulation and suppression of DNA synthesis in lymphoid cells. I. Characterization of ATP responsive cells in mouse lymphoid organs. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1834–1838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Nakazawa K., Ohara-Imaizumi M., Obama T., Fujimori K., Takanaka A. Antagonism by reactive blue 2 but not by brilliant blue G of extracellular ATP-evoked responses in PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):851–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Picus J., Schultz T., Weiss A. Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is required for T-cell antigen receptor and CD2-mediated activation of a protein tyrosine kinase and interleukin 2 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2037–2041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Shiau A. K., Brake A. J., Julius D. Expression cloning of an ATP receptor from mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane D. E., Mills D. C. The effects of ATP on platelets: evidence against the central role of released ADP in primary aggregation. Blood. 1975 Sep;46(3):309–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Min H. K., Rhee S. G. Inhibition of CD3-linked phospholipase C by phorbol ester and by cAMP is associated with decreased phosphotyrosine and increased phosphoserine contents of PLC-gamma 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1496–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotton S., Raspe E., Demolle D., Erneux C., Boeynaems J. M. Involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and calcium in the action of adenine nucleotides on aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17461–17466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Kinetic differences between thrombin-induced and ADP-induced calcium influx and release from internal stores in fura-2-loaded human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeant P., Farndale R. W., Sage S. O. ADP- and thapsigargin-evoked Ca2+ entry and protein-tyrosine phosphorylation are inhibited by the tyrosine kinase inhibitors genistein and methyl-2,5-dihydroxycinnamate in fura-2-loaded human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18151–18156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Inhibition of human natural killer cell reactivity by exogenous adenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):146–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroo M., Goff L., Biffen M., Shivnan E., Alexander D. CD45 tyrosine phosphatase-activated p59fyn couples the T cell antigen receptor to pathways of diacylglycerol production, protein kinase C activation and calcium influx. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4887–4897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Kingston R., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic cultures. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):181–184. doi: 10.1038/337181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., McFall P., Morgan R., Link M., Hecht F., Cleary M., Sklar J. Long-term growth of malignant thymocytes in vitro. Blood. 1989 Jun;73(8):2182–2187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Morgan R., Gemmell R., Amylon M. D., Link M. P., Linker C., Hecht B. K., Warnke R., Glader B. E., Hecht F. Clinical and biologic characterization of T-cell neoplasias with rearrangements of chromosome 7 band q34. Blood. 1988 Feb;71(2):395–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., McMillian M. K., Talamo B. R. Coomassie Brilliant Blue G is a more potent antagonist of P2 purinergic responses than Reactive Blue 2 (Cibacron Blue 3GA) in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1279–1285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92741-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. J., Cunningham G. R., Strupp J. A., House F. S., Kelley L. L., Henderson G. S., Exton J. H., Bocckino S. B. Activation of phospholipase D: a signaling system set in motion by perturbation of the T lymphocyte antigen receptor/CD3 complex. Cell Regul. 1991 Oct;2(10):841–850. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.10.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. G., Cantrell D. A. Heterogeneity of the regulation of phospholipase C by phorbol esters in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3523–3528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yule D. I., Wu D., Essington T. E., Shayman J. A., Williams J. A. Sphingosine metabolism induces Ca2+ oscillations in rat pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12353–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Moatassim C., Dornand J., Mani J. C. Extracellular ATP increases cytosolic free calcium in thymocytes and initiates the blastogenesis of the phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-treated medullary population. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 11;927(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Moatassim C., Dubyak G. R. A novel pathway for the activation of phospholipase D by P2z purinergic receptors in BAC1.2F5 macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23664–23673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]