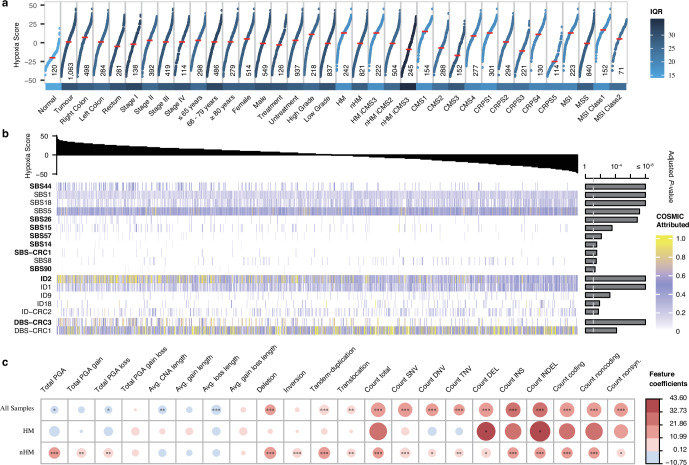
Extended Data Fig. 8. Hypoxia in colorectal cancer is associated with mismatch repair deficiency and genomic structural variation.
a, Hypoxia scores based on the Buffa mRNA abundance signature for 1,063 tumour and 120 normal CRC tissues, displayed by clinical, genomic and transcriptomic features. For each group, the median hypoxia score is marked (horizontal red line) and variability is coloured according to the interquartile range (IQR). b, Association of hypoxia score (top) with mutational signatures (bottom) coloured by normalized COSMIC signature activity attributed to each sample. Adjusted FDR P-values shown to the right and significance threshold indicated by dotted line (F-test full and null models’ comparison, FDR < 0.05). Signatures that showed positive correlation with the hypoxia score are shown in bold, the remainder showed negative correlation with the score. c, Association of hypoxia scores with somatic structural variants, displayed by hypermutation status. Size and colour of the dots represent regression coefficients of the full model * FDR < 0.05, ** FDR < 0.01, *** FDR < 0.001 (F-test full and null models’ comparison). IQR, interquartile range; PGA, percentage of genome with copy number alterations; CNA, copy number alterations; SNV, single nucleotide variation; DNV, double nucleotide variation; TNV, triple nucleotide variation; DEL, deletion; INS, insertion; INDEL, insertion and deletion.