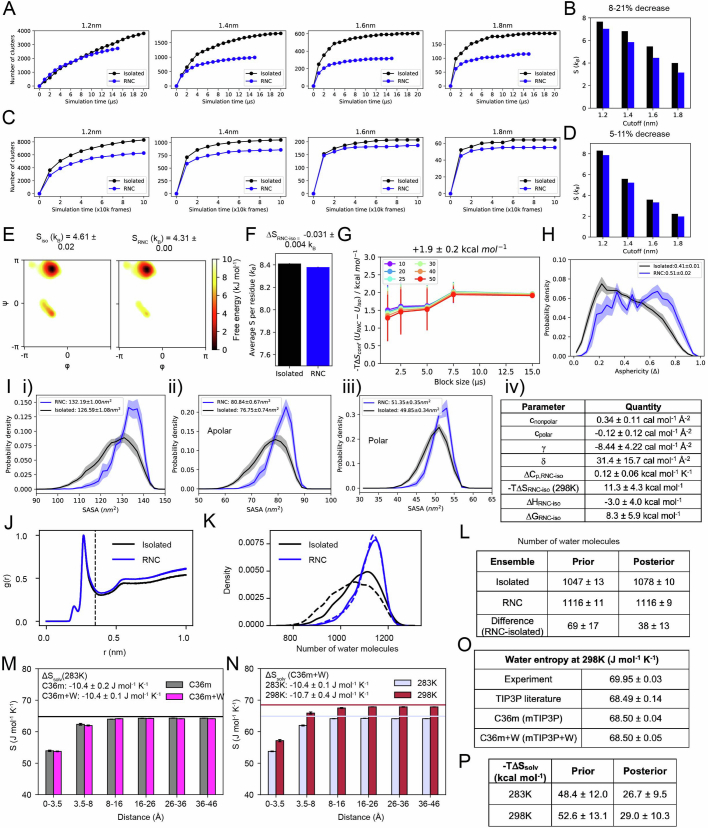
Extended Data Fig. 6. Entropy analysis of the unfolded state on and off the ribosome.
(A) Convergence of the number of clusters visited (see methods for clustering details) for several different cut-off values was assessed by plotting number of clusters as a function of simulation time. This confirmed that for the higher cut-off values (1.4–1.8 nm), sampling has been sufficient to reach a plateau in the number of clusters visited. This was analysed to ensure that differences between the RNC and isolated protein are not due to differences in sampling. (B) The average Gibbs entropy (, where n is the number of clusters/microstates and p the population of each microstate) was then estimated from the full ensembles after reweighting with the PRE data. (C) and (D) show the same analysis as in panels A-B but for a simple all-atom steric model of the unfolded state (see Methods). (E) Exemplar Ramachandran free energy landscapes of A721 on and off the ribosome. (F) The average entropy (S) summed over all residues for each ensemble is shown (mean ± SEM from block averaging). The average difference per residue is shown above the plot. Structures were sampled every 20 ps with equal statistical weights (to avoid differences due to differences in reweighting between the ensembles). (G) The resulting effect on free energy (−TΔS for the entire protein at 298 K, mean ± SEM) was calculated using different block sizes of total sampling and number of bins (legend of plot). We observe a convergence towards +1.9 ± 0.2 kcal mol−1 (estimated from 7.5 μs sampling and 50 bins). (H) Asphericity (Δ, see methods) of the ensembles shown as probability distributions (mean ± SEM from block averaging). (I) Probability distribution (mean ± SEM from block averaging) of the total (i), apolar (ii) and polar (iii) solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) of FLN5 (residues 646–750) is shown for each ensemble. (iv) The thermodynamic parameters of the solvation free energy difference between the unfolded state on and off the ribosome were calculated based on the apolar and polar changes in surface area and experimentally-parameterised functions of the heat capacity, Cp, entropy, S, and enthalpy, H75,134,135 (see methods for more details). (J) Average radial distribution function of the protein (all atoms) to water (centre of mass) distance for the isolated and RNC ensemble. The vertical line represents the 3.5 Å distance cut-off chosen to define the hydration layer consisting of the first and second hydration shell. (K) Probability distributions of the number of water molecules in the first hydration layer before (dashed line) and after (solid line) reweighting with PRE-NMR data and (L) ensemble-averaged number of water molecules in the hydration layer (mean ± SEM from block averaging). (M) Molar water entropy of obtained with the two-phase thermodynamic method (2PT) as a function of distance from the FLN5 A3A3 protein at 283 K for both the C36m and C36m+W parameters (which differ only in their water hydrogen LJ parameter). The horizontal line represents the bulk molar entropy of water obtained from a pure water box at 283 K (panel O). The solvation entropy (Ssolv) is the difference of the molar entropy of water in the hydration layer (0–3.5 Å) and in bulk (36–46 Å value used). Values are shown as mean ± SEM obtained from five independent simulations (n = 5, see Methods). (N) Molar water entropy as a function of distance from the FLN5 A3A3 protein with the C36m+W force field at 283 and 298 K (mean ± SEM from n = 5). Their respective bulk values obtained from pure water boxes (panel P) are shown as horizontal lines. (O) Comparison of molar entropy of water obtained from experiments142, in previous work in the literature with the TIP3P water model136, and values obtained in this work with C36m and C36m+W at 298 K (mean ± SEM form n = 5). (P) Difference in solvation entropy on and off the ribosome (RNC-isolated, mean ± SEM) obtained by using the solvation entropies per water molecule from panel N and difference in the number of water molecules in the hydration shells of the RNC and isolated ensemble (see methods). This quantity is shown for the ensembles before (prior) and after (posterior) reweighting with PRE-NMR data.