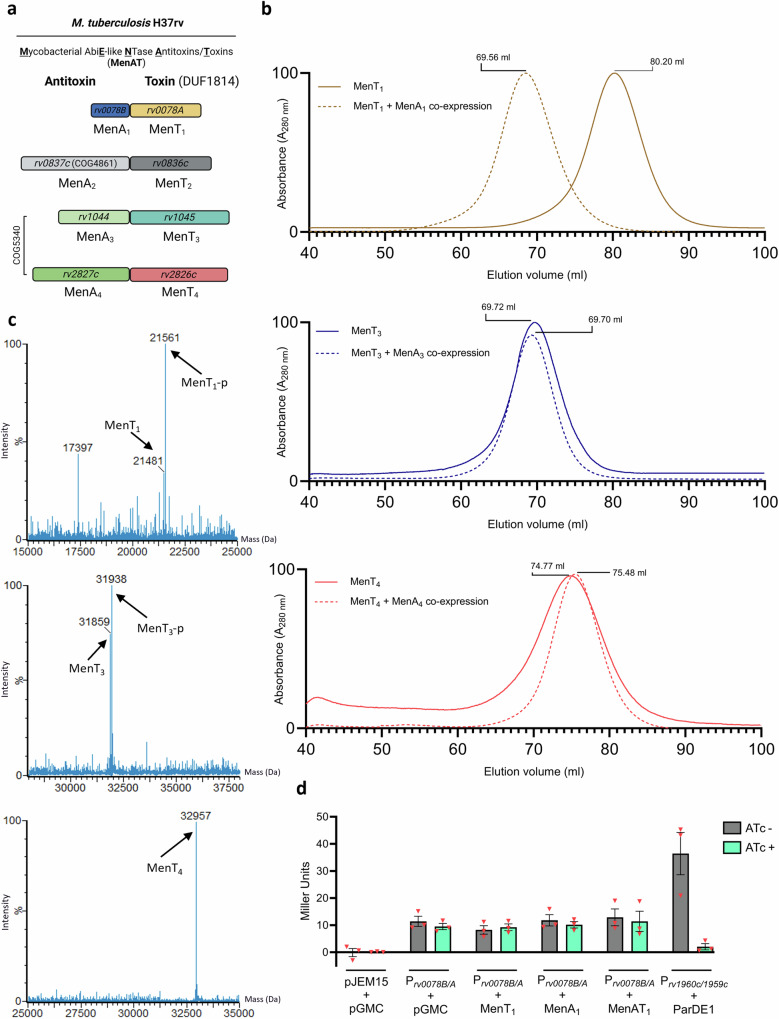
Fig. 1. MenAT systems differ in their modes of antitoxicity and regulation.
a Scaled representation of the M. tuberculosis MenAT TA systems with original gene identifiers and revised nomenclature for gene products. b Top to bottom; overlaid SEC traces of MenT1, MenT3, and MenT4 expressed and purified in the absence and presence of cognate MenA antitoxins. Chromatograms are normalized between 0 and 100 for presentation and comparison, cropped to the appropriate scale. Samples were analysed using a HiPrep™ 16/60 Sephacryl® S-200 HR column. c ES+-ToF MS of purified MenT1, MenT3, and MenT4 expressed in the presence of cognate MenA antitoxins. d β-galactosidase activity of M. smegmatis mc2−155 co-transformed with pJEM15 -vector, pJEM15-Prv0078B/A, or pJEM15-Prv1960c/1959c, and either pGMC -vector, pGMC -MenT1, -MenA1, -MenAT1, or –ParDE1. Data are representative of three independent biological replicates and bars display mean values +/- SEM.