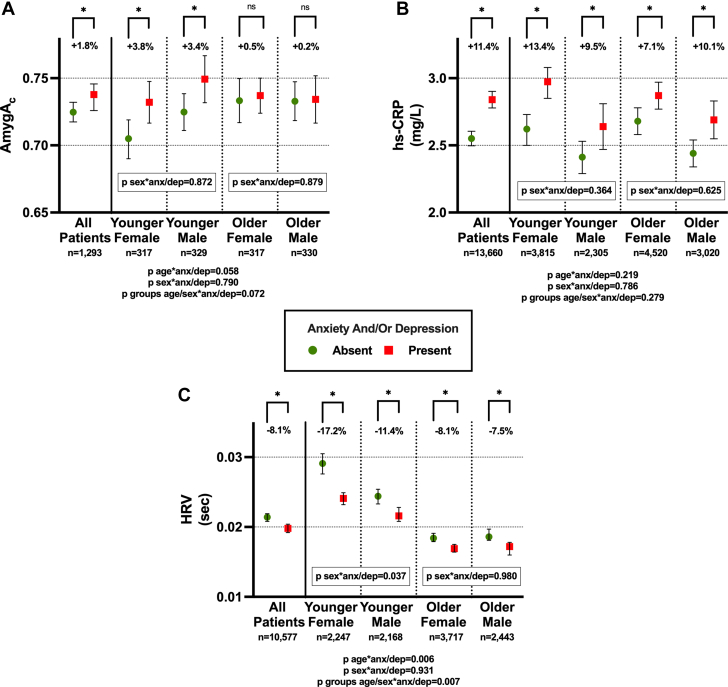
Figure 3.
Age and Sex Modify the Relationship Between Psychiatric Conditions and Neuro-immune Pathways
(A) In younger participants, the presence of pre-existing anxiety and/or depression tends to determine a greater increase in AmygAc (P for interaction = 0.058). (B) Although younger females have the greatest relative increase in hs-CRP levels when pre-existing depression/anxiety is present, neither age nor sex significantly modified the impact of depression/anxiety on hs-CRP. (C) In younger participants, the presence of pre-existing anxiety and/or depression determined a significantly greater increase in HRV (P for interaction = 0.06). Among these, the effect is stronger in female (P for interaction = 0.037). Mean values of AmygAc, HRV, and CRP are reported. Error bars represent 95% CI. Age is divided according to the median age of each study cohort. ∗P < 0.05; anx/dep = anxiety and/or depression; AmygAc = amygdalar to ventromedial prefrontal cortical activity ratio; HRV = heart rate variability; hs-CRP = high sensitivity C-reactive protein; ns = not significant