Fig 5. Measuring Cryptococcus perimeter size and distribution of cell type.
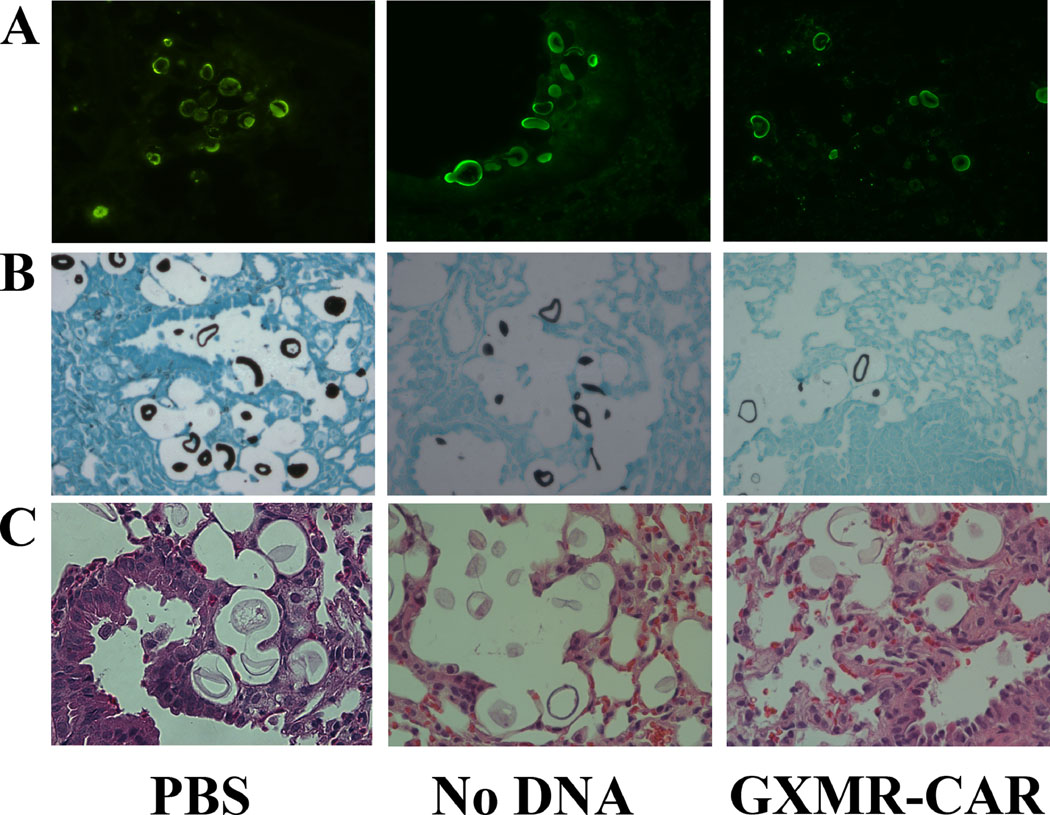
Nanozoomer software was used to measure the Cryptococcus yeast size from GMS-stained slides and categorized into 3 cell types (yeast): <50 μm, ≥51 to <90 μm (titan cell), and >91 μm (giant cell) in the PBS, NoDNA, and GXMR-CAR T cell–treated groups. (A) The perimeter size <50 μm was plotted in the upper panel and >50 μm in the lower panel. (B) Frequency distributions of cell types categorized into <50 μm; >51 μm to >90 μm, and >91 μm in PBS-treated, NoDNA T cell–treated, and GXMR-CAR T cell–treated groups are shown in (C). Distribution co- efficient shows significant differences between the cell types in the GXMR-CAR T cell–treated group; giant cells were not observed in the group. (D) Plasma of mice infected with C. neoformans and treated with PBS, NoDNA cells or GXMR-CAR T cells were obtained after infection and the levels of IFN-γ were measured using a Bio-Plex Human Cytokine Assay (Bio- Rad, Hercules, CA).
