Figure 3.
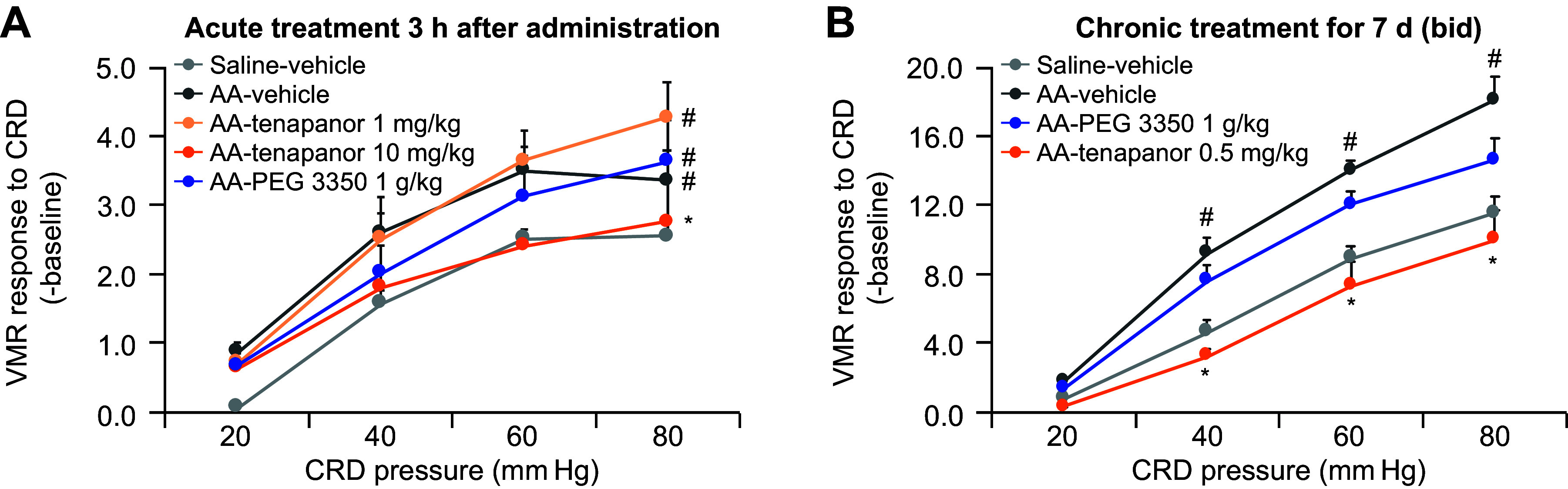
Effects of acute (A) and chronic (B) treatment of a Sprague-Dawley rat model of IBS induced by neonatal acetic acid sensitization. Rats were treated orally with tenapanor (1 or 10 mg/kg), MiraLAX (1,000 mg/kg), or vehicle (n = 6 or 7/cohort). Acute and chronic tenapanor treatment decreased pain responses as measured by a decrease in VMR to CRD vs. sensitized, vehicle-treated rats. Acute and chronic MiraLAX treatment of sensitized rats still resulted in increased pain responses vs. nonsensitized, vehicle-treated rats. Data are presented as means ± SE. Two-way ANOVA showed P < 0.05 for the main effects of treatment and pressure. #Significant difference from saline-vehicle group with overall comparison (A) or at same pressure (B); *significant difference from AA-vehicle with overall comparison (A) or at same pressure (B). AA, acetic acid; ANOVA, analysis of variance; bid, twice daily; CRD, colorectal distension; IBS, irritable bowel syndrome; VMR, visceral motor reflex.
