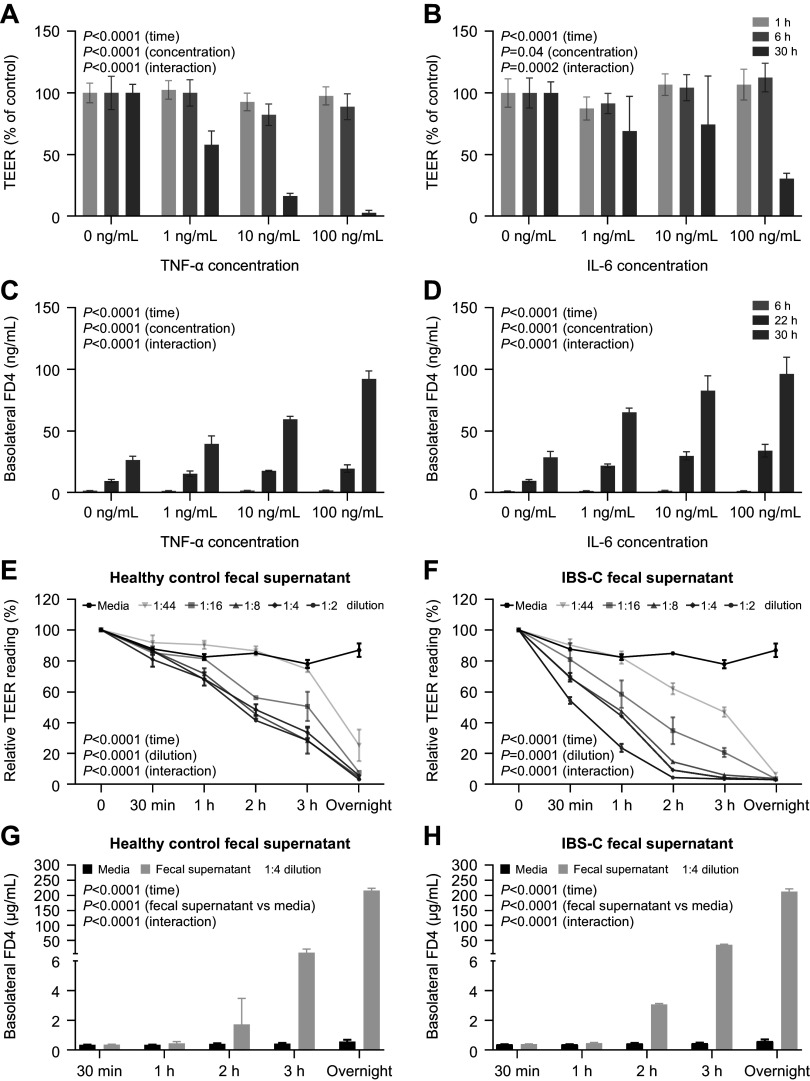
Figure 6.
Treatment of human colon monolayers with cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 resulted in a dose- and time-dependent decrease in TEER (A and B) and increase in FITC-dextran permeability (C and D). Treatment of human colon monolayers with fecal supernatants from healthy controls (n = 10) and patients with IBS-C (n = 9) results in dose- and time-dependent reductions in TEER (E and F) and increases in FITC-dextran permeability (G and H). Data are presented as mean ± SD. P values were calculated using a two-way, repeated-measures ANOVA. ANOVA, analysis of variance; FD4, fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran; FITC, fluorescein isothiocynate; IBS-C, irritable bowel syndrome with constipation; IL-6, interleukin 6; TEER, transepithelial electrical resistance; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.