Figure 8.
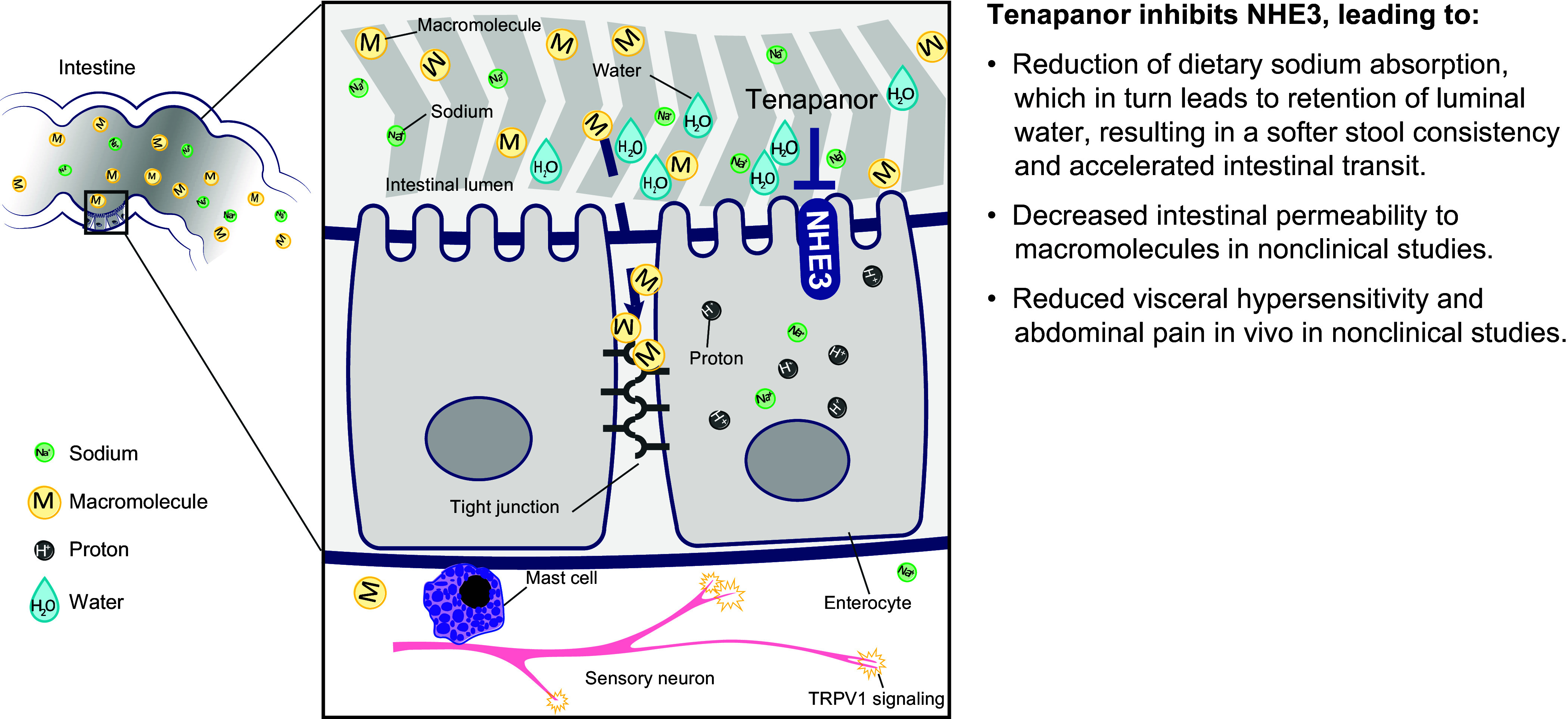
Schematic of proposed mechanism of action of tenapanor. Tenapanor inhibits NHE3, producing multiple downstream effects in the digestive tract. Reduction in dietary sodium intake leads to increased luminal water retention, allowing for faster gastrointestinal transit. Tenapanor also decreases intestinal permeability to macromolecules and antigens and reduces abdominal pain signaling. NHE3, sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 3; TRPV1, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1.
