Fig. 1. Comparison of the structural complexities of naturally occurring and de novo designed proteins.
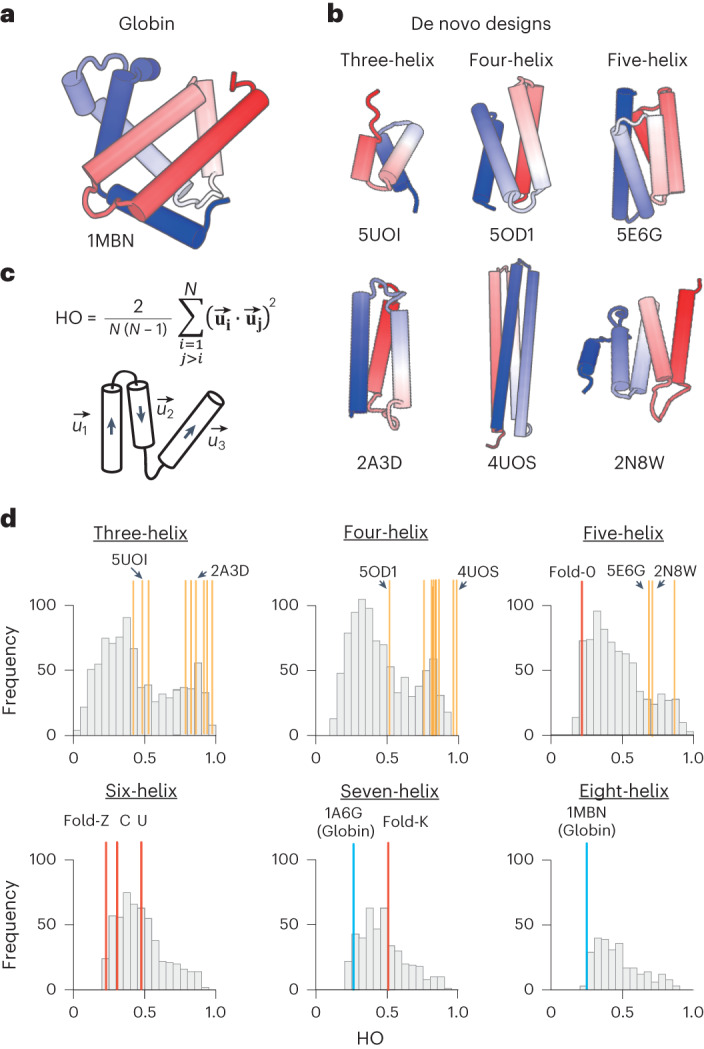
a,b, Structures of myoglobin (a) and representative de novo designed all-α proteins (b) (the N- and C-terminals are colored in blue and red, respectively, and the characters represent PDB IDs). The α-helices in the globin structure are irregularly aligned, whereas those of the de novo designs are almost parallelly aligned. c, The order parameter capturing the complexities of α-helical proteins, HO. HO is defined by the average of inner products between helix orientation vectors, ui, for all pairs of N α-helices55. Higher values indicate more ordered, and lower values more complicated. d, HO distributions for naturally occurring and de novo designed proteins with three to eight α-helices. Whereas naturally occurring all-α proteins show broad distributions irrespective of the number of constituent α-helices, previous de novo designed all-α proteins indicated by yellow-ocher bars show relatively higher values in the distributions (for details of the previous designs, see Extended Data Fig. 1). Notably, globin structures indicated by blue bars have quite low values. The all-α proteins created in this study, indicated by red bars, have lower values than the previous designs.
