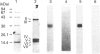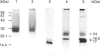Abstract
A protein extract of mouse seminal-vesicle secretion was used to immunize mature mice (Balb/c) of both sexes. Results of Western-blot analyses for these secretory proteins indicated that only one minor protein component could be recognized by the autoantisera prepared from either autoimmunization of male mice or isoimmunization of female mice. The autoantigen was purified from seminal-vesicle secretion. The purified autoantigen retained the ability to induce autoantibody formation. The autoantigen has glycoprotein characteristics: the majority of the carbohydrate is N-linked and the remainder is O-linked. Rabbit antibodies to the autoantigen were used to isolate the corresponding cDNA from a mouse seminal-vesicle cDNA library. The primary structure deduced from the cDNA sequence was confirmed by direct amino acid sequence determination. The results indicate that the core protein consists of 131 amino acid residues. Analysis of the primary structure indicates that the autoantigen has two potential acceptor sites for the N-linked carbohydrate at Asn-12 and Asn-122, three potential phosphorylation sites for casein kinase II at Thr-55, Ser-68 and Thr-76, and three potential phosphorylation sites for protein kinase C at Thr-28, Thr-40 and Thr-124. The core protein and the carbohydrate portion together have a molecular mass of 19 kDa. Results from Western- and Northern-blot analyses for various tissues indicate that the seminal vesicle is the sole organ producing this autoantigen. Expression of this autoantigen gene was stimulated by testosterone.
Full text
PDF

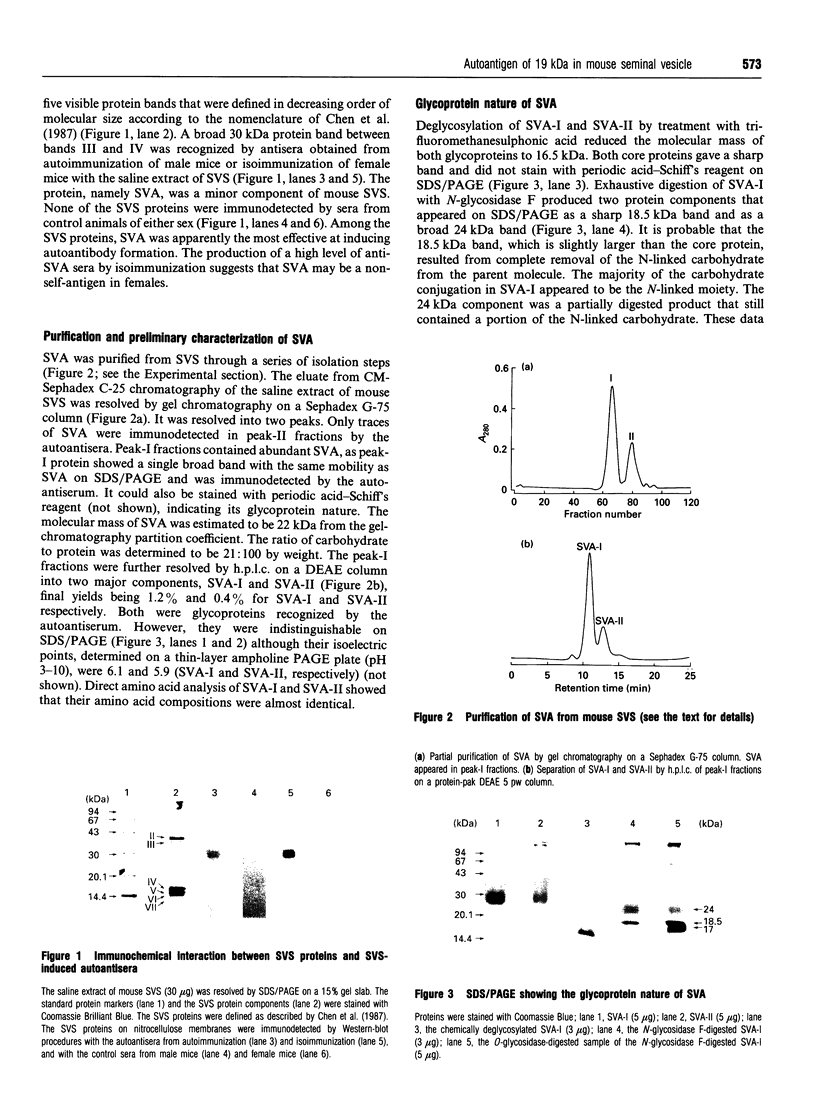



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Pentecost B. T., McLachlan J. A., Teng C. T. The androgen-dependent mouse seminal vesicle secretory protein IV: characterization and complementary deoxyribonucleic acid cloning. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Oct;1(10):707–716. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-10-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge A. S., Faltynek C. R., Hof L., Reichert L. E., Jr, Weber P. Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavel Y., von Heijne G. Sequence differences between glycosylated and non-glycosylated Asn-X-Thr/Ser acceptor sites: implications for protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1990 Apr;3(5):433–442. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Nishiyama K., Nakanishi H., Uratsuji Y., Nomura H., Takeyama Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on the phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by protein kinase C and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12492–12499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. L., Chen S. W., Chen Y. H. Purification and characterization of a trypsin inhibitor from mouse seminal vesicle secretion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Nov 1;290(2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90540-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansson P. E., Sugino A., Harris S. E. Use of a cloned double stranded cDNA coding for a major androgen dependent protein in rat seminal vesicle secretion: the effect of testosterone in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):935–946. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski M. C., Kistler M. K., Kistler W. S. Purification and cell-free synthesis of a major protein from rat seminal vesicle secretion. A potential marker for androgen action. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Elder J. H., Alexander S., Phelan A. W., Tarentino A. L. Demonstration of peptide:N-glycosidase F activity in endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F preparations. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10700–10704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., Uchida T., Mewes H. W., Ataka T. A rapid vapor-phase acid (hydrochloric acid and trifluoroacetic acid) hydrolysis of peptide and protein. J Biochem. 1987 Dec;102(6):1593–1597. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto J., Bhavanandan V. P., Davidson E. A. Purification and properties of an endo-alpha-N-acetyl-D-galactosaminidase from Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8609–8614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]