Fig. 5.
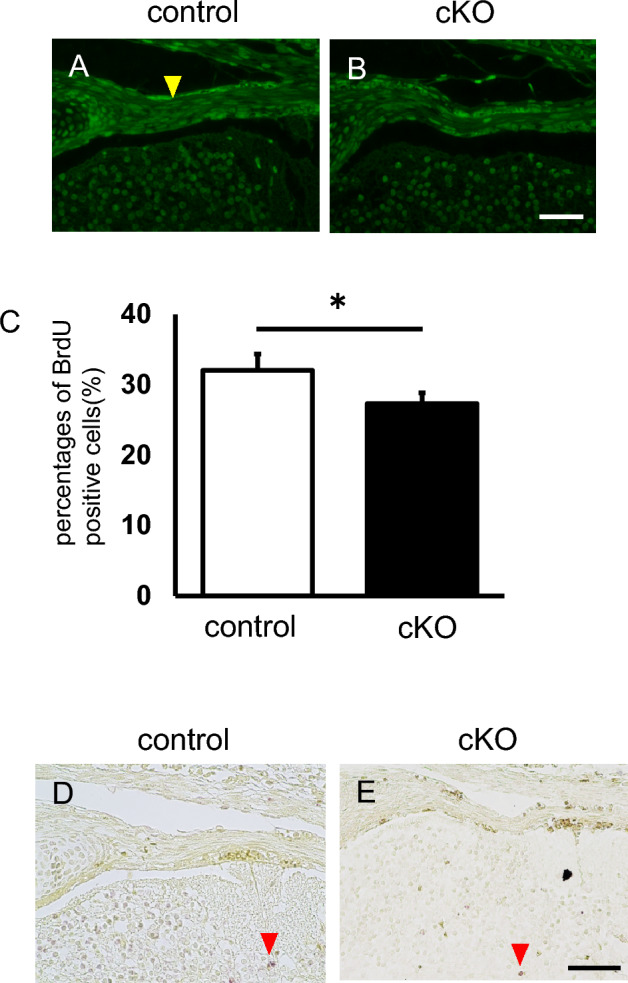
G9a deletion inhibits proliferation but does not affect apoptosis in developing tendons. BrdU was injected at E16.5 and recovered at E17.5. BrdU incorporation was assessed in the vertebral tenocytes of control (A, G9afl/+; Sox9Cre/+) and G9a cKO mice (B, G9afl/fl; Sox9Cre/+) by using an anti-BrdU antibody (control n = 2; cKO n = 2). Immunofluorescence images of BrdU-labeled cells are shown. The yellow arrowheads indicate strongly positive cells. Bar = 50 μm. (C) Comparison of the percentages of BrdU-positive cells (n = 3). We counted 60–64 cells/section and three independent sections were analyzed (*p < 0.05, t-test). (D and E) TUNEL staining in vertebral tenocytes of control (D, G9afl/+; Sox9Cre/+) and G9a cKO (E, G9afl/fl; Sox9Cre/+) mouse embryos at E16.5. Red arrowheads indicate apoptotic nuclei. Bar = 50 μm.
