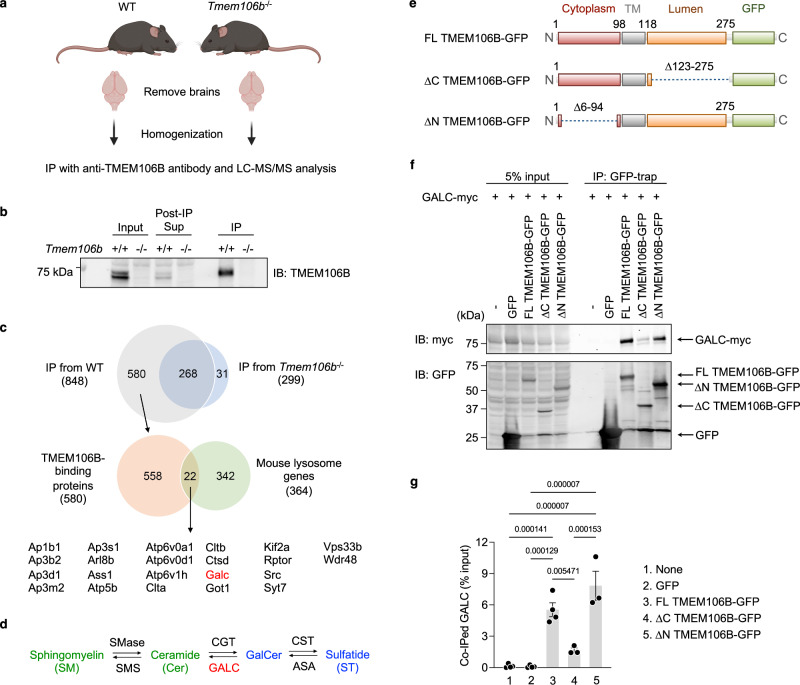
Fig. 4. TMEM106B physically interacts with GALC via its luminal region.
a Diagram showing experimental procedures of IP and LC-MS/MS analysis using mouse brains. The diagram was created with BioRender.com. b Representative blots to validate immunoprecipitation of endogenous TMEM106B from mouse brains using anti-TMEM106B antibody linked to protein A Sepharose. Note that all samples were run without treating with 2-mercaptoethanol and heat. c Venn diagrams to identify potential lysosomal TMEM106B-binding proteins. Total 848 proteins were identified in immunoprecipitates from WT brains but 268 of them were also found in those from TMEM106B-deficient brains. Thus, 580 proteins were considered as potential TMEM106B-binding proteins. Among them, 22 proteins were lysosomal proteins based on The Mouse Lysosomal Gene Database (http://lysosome.unipg.it/mouse.php). d Biosynthesis and degradation of GalCer and ST. SMase sphingomyelinase, SMS sphingomyelin synthase, CGT cerebroside galactosyl transferase, CST cerebroside sulfotransferase, ASA arylsulfatase A. TMEM106B deficiency results in a decrease in levels of GalCer and ST (blue) while having no effects on levels of Cer and SM (green). e Schematic drawing of full-length (FL) TMEM106B-GFP and TMEM106B-GFP lacking amino acids (aa)123–275 (ΔC) and aa6–94 (ΔN). f Representative blots of co-IP assays using HEK293T cells expressing GFP, FL TMEM106B-GFP, ΔC TMEM106B-GFP, or ΔN TMEM106B-GFP, together with myc-DDK-tagged mouse GALC. Note that all samples were treated with 2-mercaptoethanol and heat (95 °C) before running a gel. Monomeric TMEM106B-GFP fusion protein was detected at ~70 kDa (~43 kDa glycosylated TMEM106B + ~27 kDa GFP). g Quantification of co-IP in (f). Mean ± SEM, n = 3–4 experiments. p-Values were determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test and were shown on the top of the graph.