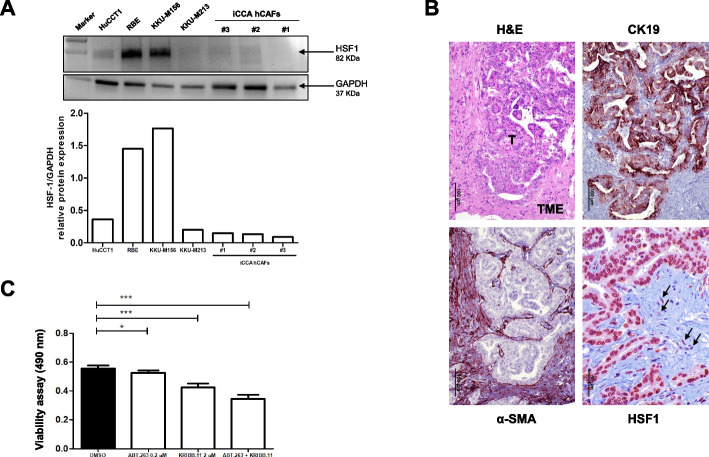
Fig. 10.
The HSF1 inhibitor KRIBB-11 reduces the growth in vitro of human cancer-associated fibroblasts. A Levels of HSF1 in human HuCCT1, RBE, KKU-M156, and KKU-M213 intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) cell lines, and in human cancer-associated fibroblasts (hCAFs), as determined by Western blot analysis. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping protein and protein values of each sample are reported below. B Representative immunohistochemistry showing immunoreactivity for HSF1 in the tumor (T) and the tumor microenvironment (TME) compartments. Arrows indicate fibroblasts showing moderate immunolabeling for HSF1 protein. Alpha-smooth-muscle (α-SMA) staining was used as a tumor stroma marker, while CK19 staining was used as a biliary marker. Original magnification: 200x for H&E, CK19, and α-SMA; 400x for HSF1; scale bar: 100 μm for H&E, CK19, and α-SMA; 50 μm for HSF1. Abbreviations: H&E, hematoxylin and eosin staining. C The co-treatment with ABT-263 and KRIBB-11 inhibits the cell viability in iCCA hCAFs. Effect of ABT-263, KRIBB-11, and their co-administration on the viability of iCCA hCAFs, grown for 72 h in culture medium supplemented with 10% FBS. Note the higher anti-growth effects of the two combined drugs than single treatments. Experiments were repeated three times in triplicate. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001, as calculated with a One-way ANOVA test