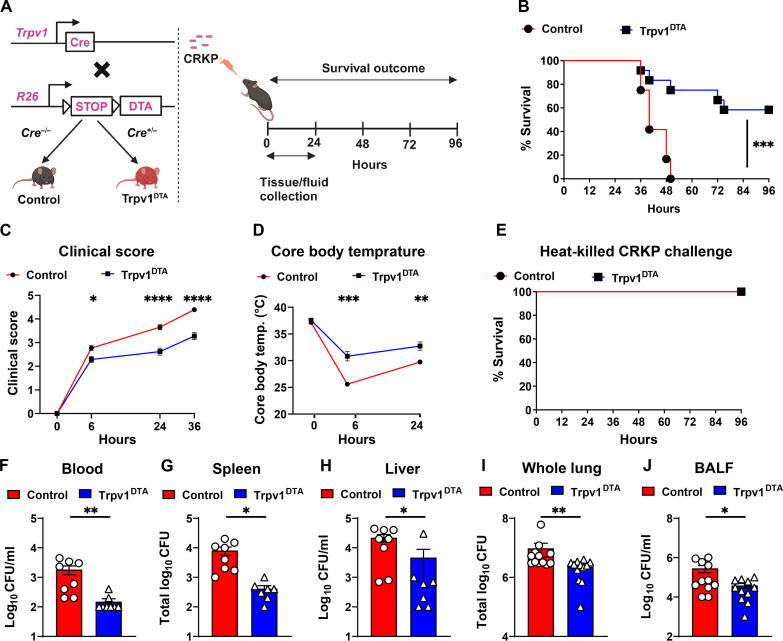
Fig. 1. Nociceptor neurons suppress host protection against CRKP pneumonia and pneumonic sepsis.
(A) Genetic strategy for ablating TRPV1+ neurons in mice (left) and mouse model of CRKP lung infection (right). Control and Trpv1DTA mice were infected with the lethal dose (109 CFU per mouse) of CRKP intranasally. (B to D) Survival curve (B), clinical score (C), and core body temperature (D) of control and Trpv1DTA mice over time. Data in (B) include Trpv1DTA mice (n = 12) and littermate control mice (n = 12) from three independent experiments. Data in (C) and (D) are the means ± SEM and involve Trpv1DTA mice (n = 8 to 12 mice per group) and control littermates (n = 8 to 12 mice per group). (E) Survival curve of control (n = 8) and Trpv1DTA mice (n = 8) after intranasal challenge with heat-killed CRKP bacteria (109 CFU per mouse). (F to J) CFUs recovered in blood (F), spleen (G), liver (H), whole lung (I), and BALF (J) from control and Trpv1DTA mice at 24 hpi. Each symbol denotes a mouse [(F) to (J)]. Data in (F) to (J) are the means ± SEM and at least two independent experiments with n = 7 to 12 mice per group. Statistical analysis was done by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test [(B) and (E)], two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Sidak’s multiple comparison’s test (C), repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison’s test (D), Mann-Whitney test [(F), (H), and (I)], and two-tailed unpaired t test [(G) and (J)]. Levels of significance for all statistical analyses: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. BioRender.com was used to create schematic in (A).