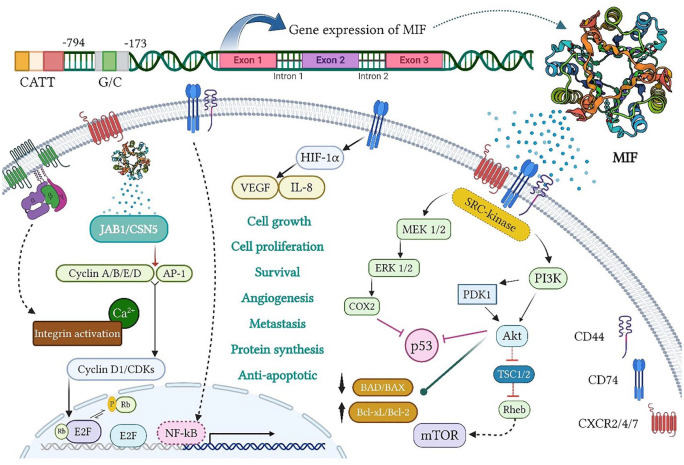
Figure 1.
MIF gene expression and biological activity. The MIF transcription from its gene on chromosome 22q11.2 includes three exons, separated by two introns, under two MIF promoters (namely, CATT5 8 and G/C), and located at 794 and 173 positions, respectively. The MIF signaling is also generated by interactions with CD74 and CD44 as well as CXCR2/4/7 on the cell surface. First, it stimulates the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK/MAPK) and phosphatidyl 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathways. The activation of ERK/cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) and PI3K/AKT also inhibits p53-dependent apoptosis and promotes tumor cell proliferation. On the contrary, the PI3K/AKT and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation causes the inactivation of pro-apoptotic proteins, BAD and BAX, and the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2, which increase the survival and invasion of cancer cells. During hypoxia, the MIF binding to CD74 contributes to the activation and stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 subunit alpha (HIF1α), which then enhances the expression of angiogenic GFs, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and IL-8, thereby promoting angiogenesis. Moreover, extracellular MIF binding to G protein-coupled chemokine receptors (GPCRs), namely, CXCR2, CXCR4, and CXCR7, individually or in a CD74-dependent manner, triggers the activation of integrin and its subsequent pathways, which play a key role in cancer cell invasion. Intracellularly, the MIF functionally interacts with cytosolic Jab1/CSN5, leading to the retention of the Skp1-Cullin1 F-box (SCF) complex in an activated form as well as the induction of cyclin activity and/or c-Jun/AP-1 phosphorylation. Meanwhile, the CD74/CD44 receptor complex releases the intracellular domain (ICD) of CD74 and translocates into the nucleus, thereby boosting nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation. MIF indicates migration inhibitory factor.