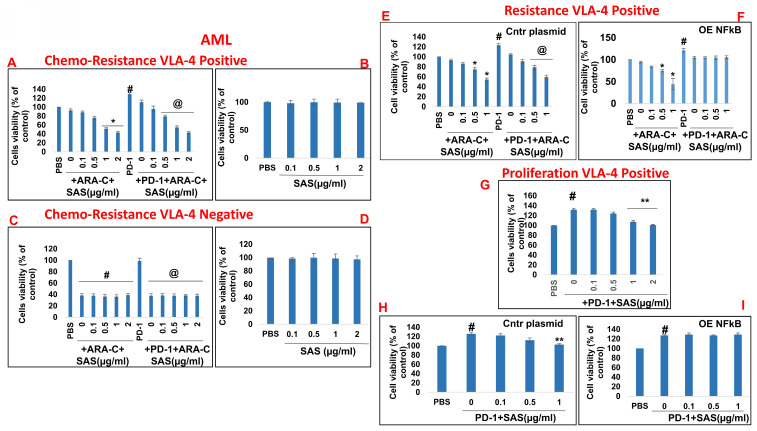
Figure 7.
Inhibition of PD-1/PD-L1-induced malignant cell chemoresistance and proliferation by SAS: (A, B, E, F) Human VLA-4-positive or (C, D) VLA-4-negative AML cells isolated from AML patients were cultured on FN-coated plates in the presence (A, C) or absence (B, D) of ARA-C (10-6M) or PD-1 (0.2 μg/ml), with or without SAS at the indicated concentrations (A-D). Some of the cells (E) were either transfected with a control plasmid or (F) overexpressing (OE) NFκB. Resistance to chemotherapy (A, C) and the dose-dependent effect of SAS alone (B, D) on cell viability were tested via the XTT viability test. #p<0.01 vs. PBS; *p<0.05 vs. ARA-C alone; @p<0.01 vs. PD-1. For proliferation assays, cells were cultured on FN-coated plates in the presence or absence of PD-1, with or without SAS at various concentrations (G-I). Some of the cells were either transfected with a control plasmid (H) or overexpressing NFκB (I). PD-1-PD-L1-induced proliferation and its inhibition by SAS were tested via XTT cell viability tests. The results represent the mean+SE of 3 experiments; #p<0.05 vs. PBS; **p<0.05 vs. PD-1. Significance was calculated via one-way ANOVA. ARA-C (Arabinosylcytosine).