Figure 4. Mrc1 histone binding activity is required for heterochromatin maintenance in S. pombe.
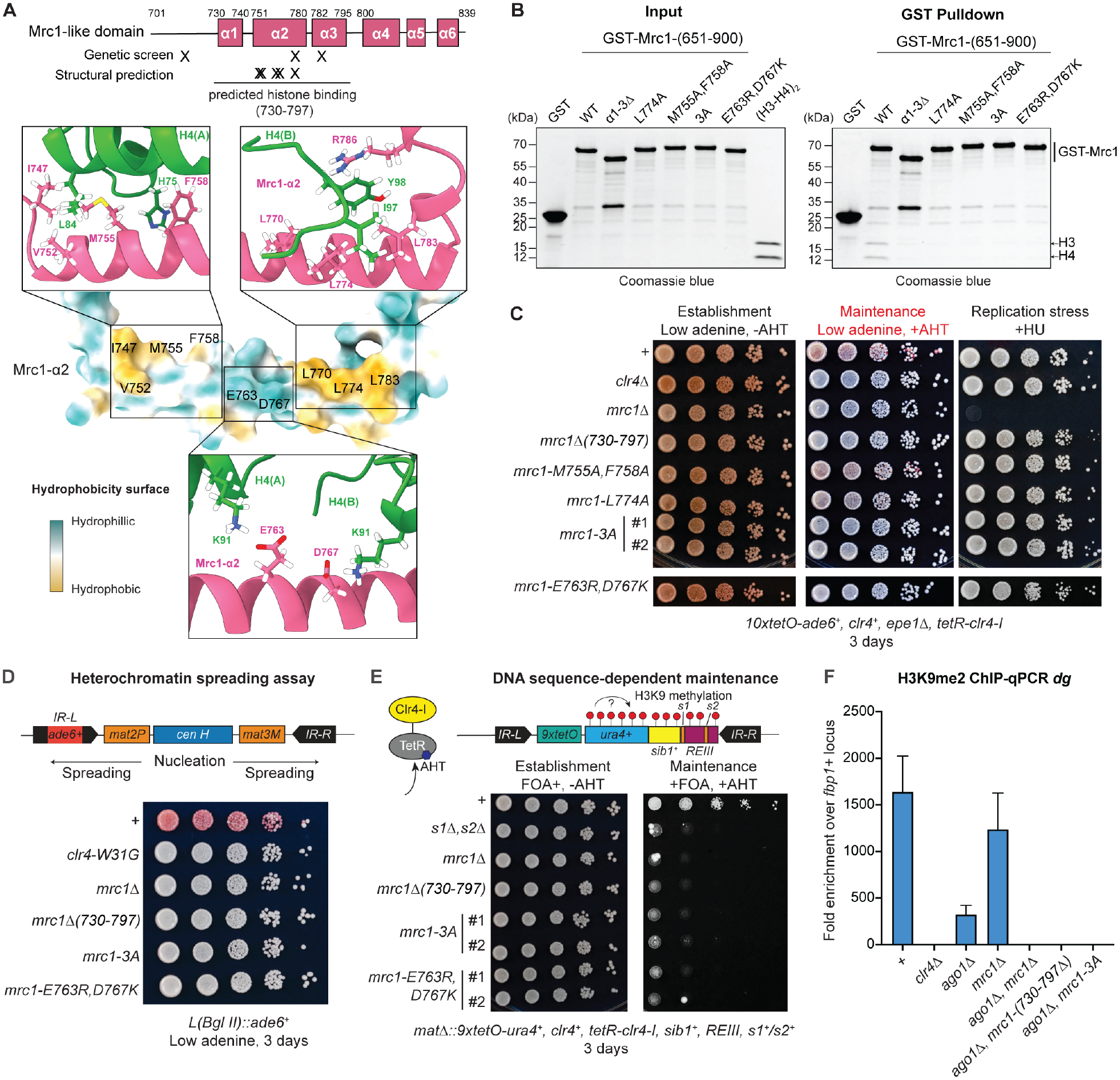
A) Energy minimized AlphaFold-predicted interaction between Mrc1-α2 and histone H4s. Top, diagram showing the location of Mrc1-α2 and the Mrc1-histone binding domain. Bottom, hydrophobic map of the Mrc1-α2 and detailed predicted interactions between Mrc1-α2 and histone H4. B) In vitro GST pulldown assays showing the effect of hydrophobic (Mrc1-M755A, F758A, L774A) and electrostatic (Mrc1-E763R, D767K) mutations in Mrc1-α2 on histone H3-H4 binding. C) Heterochromatin maintenance assay showing the phenotypes of hydrophobic and electrostatic mutations in mrc1-α2. D) Top, diagram showing the ade6+ reporter gene inserted at the boundary of the mating type locus IR-L (L(BglII)::ade6+). Bottom, silencing assays showing phenotypes of cell carrying Mrc1-histone binding domain mutations in silencing of the ade6+ reporter. E) Top, diagram showing the DNA sequence-dependent heterochromatin maintenance reporter system in S. pombe. Bottom, spotting assay showing the maintenance phenotype of the ura4+ report gene in wildtype cells and cells carrying the indicated mutations. As a control, cells with deletions of Atf1/Pcr1 binding sites (s1Δ,s2Δ) are unable to maintain heterochromatin. F) H3K9me2 ChIP-qPCR analysis of mrc1 mutations in combination of ago1Δ at pericentromere dg repeats. N=3, error bars indicate standard deviations.
