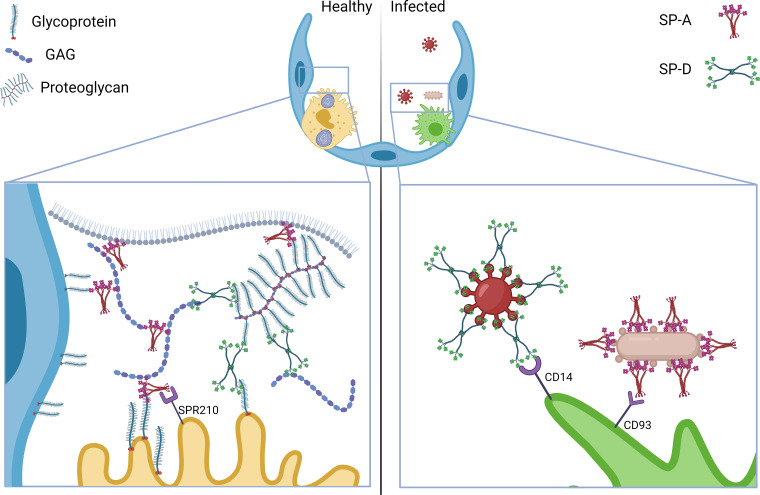
Figure 6.
Model of the proposed function of SP-A and SP-D as cross-linking proteins of the alveolar glycocalyx in healthy lung conditions (right) where SP-A and SP-D bind GAGs and interconnect free GAGs with proteoglycans and membrane glycoproteins. In addition, SP-A binds to its specific receptor SPR210 on the surface of AE2C and lipids at the air-liquid interface. In contrast, SP-A and SP-D play an important function opsonizing pathogens (left). SP-A and SP-D also bind to specific receptors at the surface of alveolar macrophages, such as CD14 and CD93. GAG, glycosaminoglycan; SP-A, surfactant protein A; SP-D, surfactant protein D. [Image created with a licensed version of BioRender.com.]