FIGURE 8.
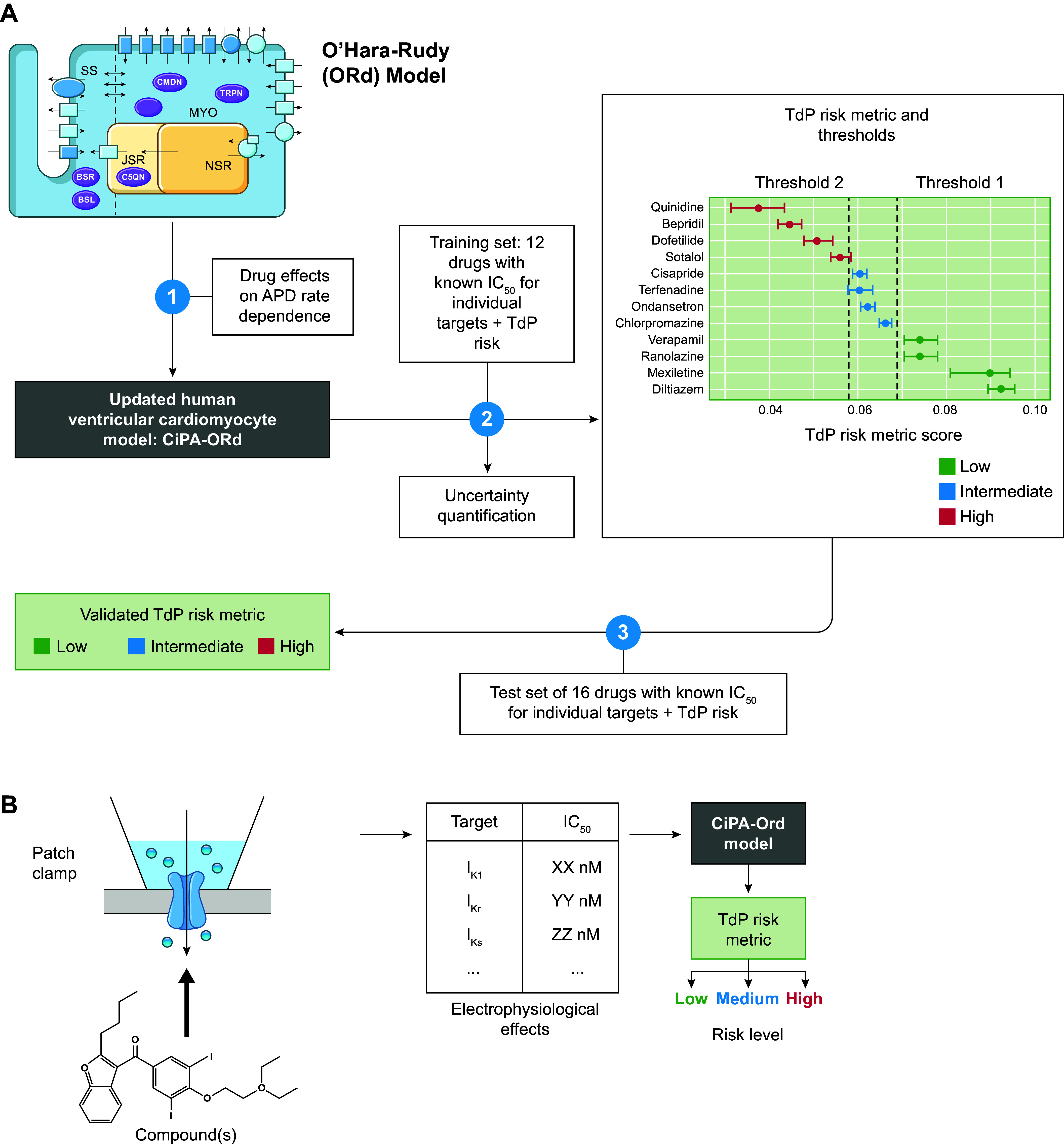
Use of cardiac cellular electrophysiology models in cardiac safety pharmacology: the Comprehensive in vitro Proarrhythmia Assay (CiPA) initiative. A: an updated version of the O’Hara et al. (67) model of the human ventricular cardiomyocyte by Dutta et al. (157) (CiPA-ORd) was used to simulate the effects of a compound on individual ion channels (step 1). A torsade des pointes (TdP) risk metric score was calculated, and thresholds for separating low-, medium-, and high-risk drugs were established based on a training set of 12 drugs with known half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50 values) for different ion channels and known clinical TdP risk (step 2). The model performance was validated in an independent set of 16 drugs (step 3). B: the model can be employed to assess the risk of new compounds based on their experimentally characterized effects on different ion channels. APD, action potential duration; IK1, basal inward-rectifier K+ current; IKr, rapid delayed-rectifier K+ current; IKs, slow delayed-rectifier K+ current.
