Figure 2.
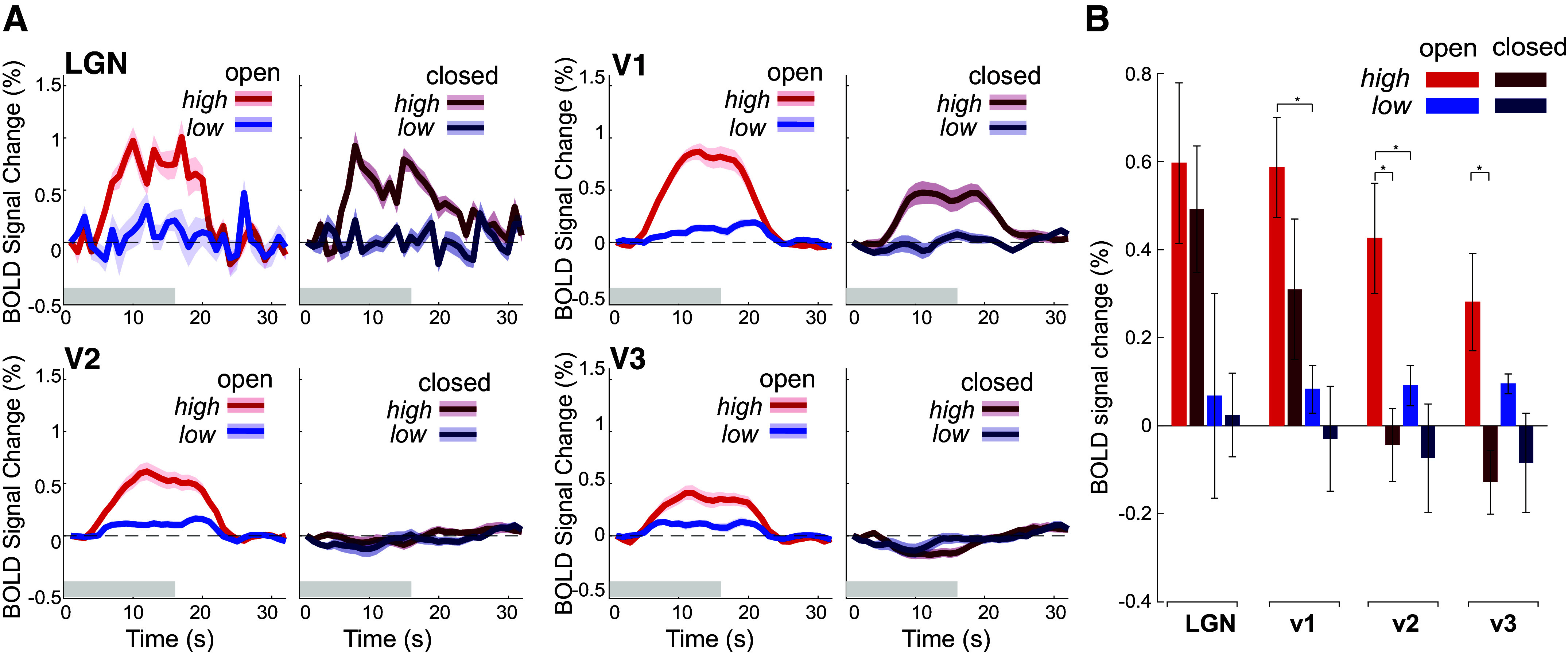
Eye closure has minimal effect on visual responses in LGN and V1, while suppressing responses in V2 and V3. A: event-triggered average for luminance task across ROI and eye condition. Across LGN, V1, and V2, during eyes open runs, high temporal contrast stimuli elicit a greater BOLD response than with low temporal contrast stimuli. Although there is no effect of temporal contrast in V3, BOLD response increases regardless of the stimulus temporal contrast. During eye closure, BOLD responses in LGN and V1 during the high temporal contrast stimuli elicit a similar BOLD response as during eyes open runs. With eye closure, V2 and V3 have strongly attenuated BOLD regardless of temporal contrast. Red plots indicate high temporal contrast trials and blue indicates the low temporal contrast trials. The gray bar indicates 16-s period of stimulus presentation. Error shading is 1 SEM. n = 8 subjects. B: average BOLD activation during stimulus presentation across conditions. Pairwise comparisons show a significant decrease in V2 and V3 BOLD magnitude with eye closure for high temporal contrast stimuli. In LGN, BOLD magnitude with high temporal contrast stimuli with eyes open was marginally greater than low contrast [t(14)=1.79; P = 0.047] at a Bonferroni corrected P value cutoff of 0.0125. In V1 with eyes closed, BOLD magnitude during high temporal contrast stimuli was marginally greater than during low temporal contrast stimuli [t(14)=1.70; P = 0.055]. In V2, BOLD magnitude with high temporal contrast stimuli with eyes open was greater than low contrast [t(14)=2.51; P = 0.012] and high temporal contrast stimuli with eyes closed were suppressed compared with eyes open. In V3, BOLD magnitude during high temporal contrast stimuli with eyes closed was also suppressed compared with eyes open. The y-axis is BOLD signal averaged across 4–16 s poststimulus onset. Error bars are 1 SEM. All P values from pairwise comparison only survive multiple comparison correction at a P value less than 0.0125, using Bonferroni correction (0.05/n where n = 4 per ROI). *P < 0.0125. BOLD, blood oxygenation level-dependent; LGN, lateral geniculate nucleus; ROI, region-of-interest; V1, primary visual cortex; V2 and V3, extrastriate visual cortex.
