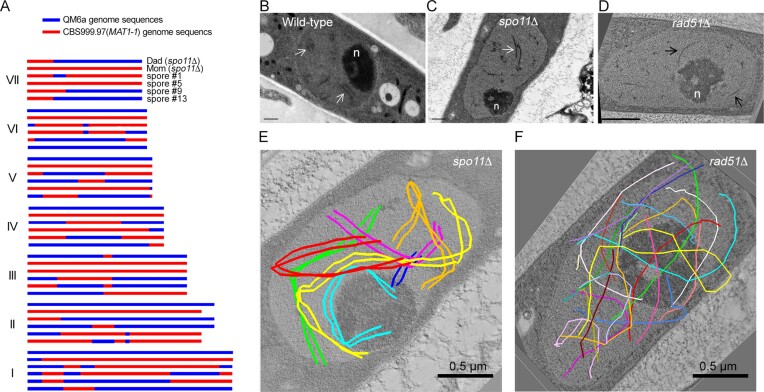
Figure 2.
spo11 is dispensable for T. reesei interhomolog recombination and chromosome synapsis. (A) Genome-wide mapping of meiotic recombination products in the absence of spo11 using PacBio Sequel technology and the TSETA software tool (59,60). The seven horizontal rows of sequence data represent the seven full-length chromosomes (I to VII) in two parental spo11Δ strains (Dad and Mom) and the four representative F1 progeny. Nucleotide sequences identical to those of the QM6a and CBS999.97(MAT1-1) reference genomes are indicated in blue and red. COs are located where 2:2 markers undergo a reciprocal genotype change. (B–D) Representative TEM images of wild-type (B), spo11Δ (C) and rad51Δ (D) meiotic cells at the pachytene stages. The SCs in WT and spo11Δ are marked by white arrows, whereas axial elements in rad51Δ are marked by black arrows. The enlarged nucleolus (n) is a hallmark of meiotic prophase nuclei. (E, F) 3D-TEM tomography. The seven pairs of lateral elements in spo11Δ (E) and the fourteen axial elements in rad51Δ (F) are highlighted as colored lines. Black bar: 0.5 μm.