Abstract
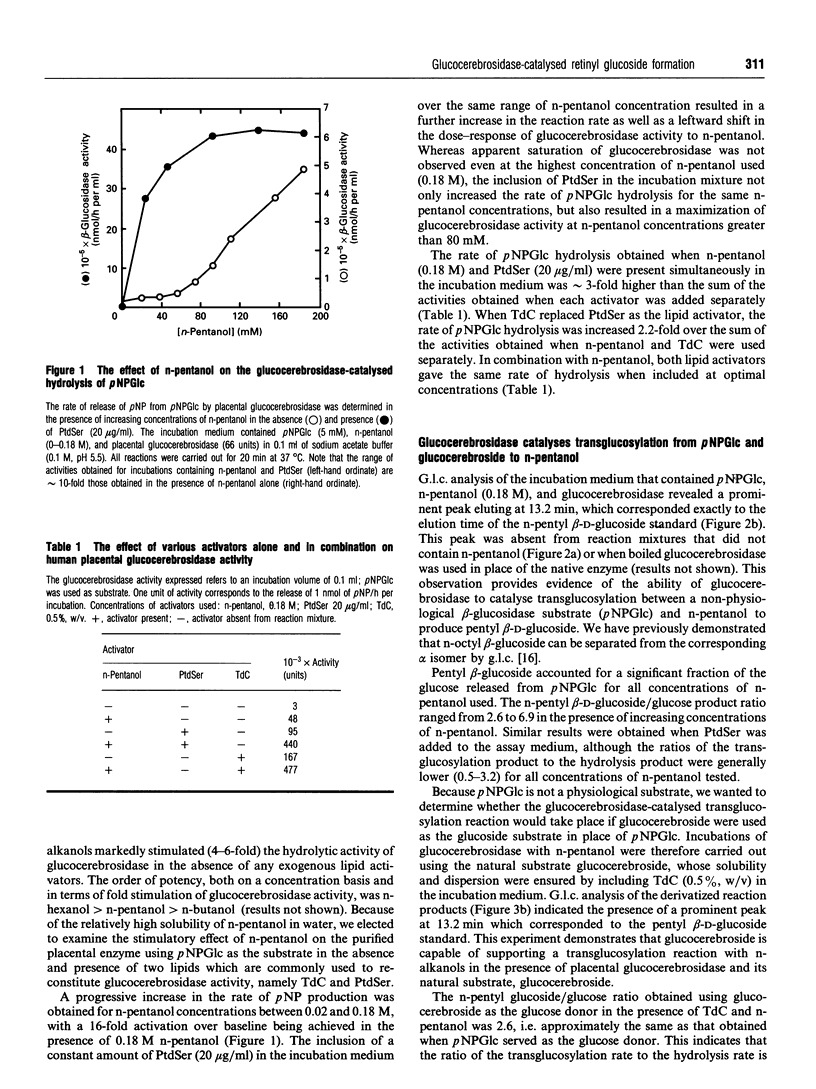
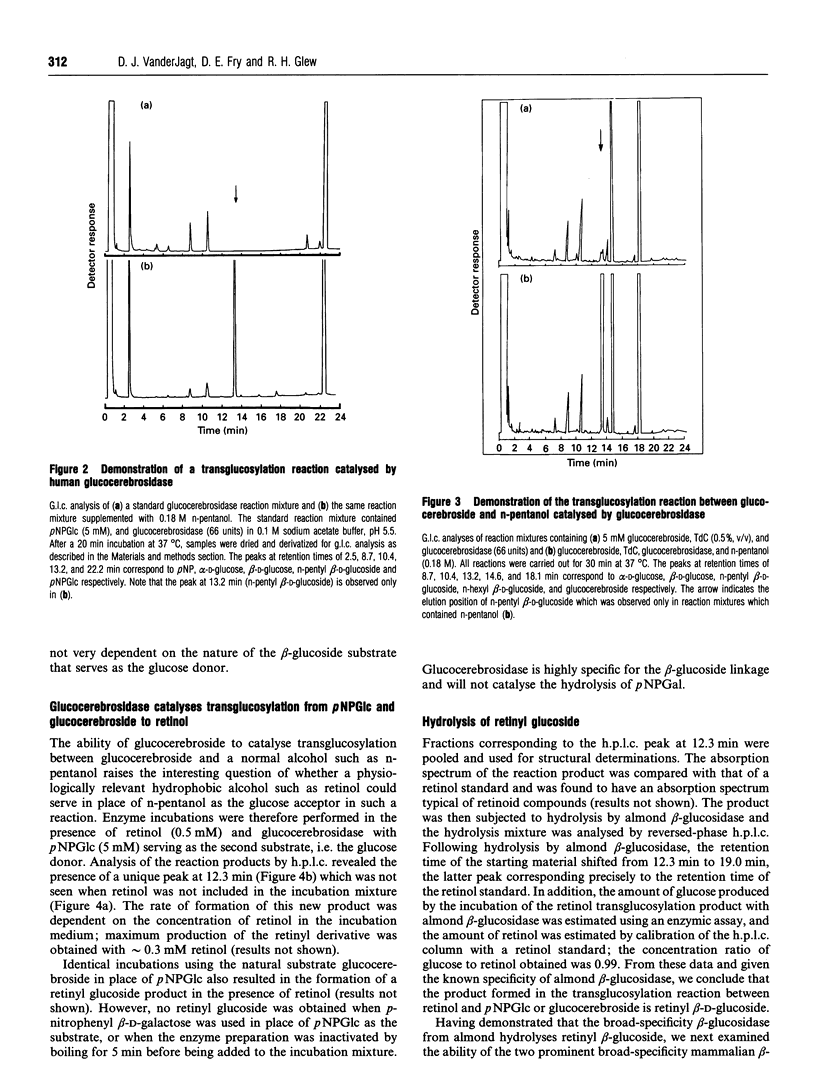
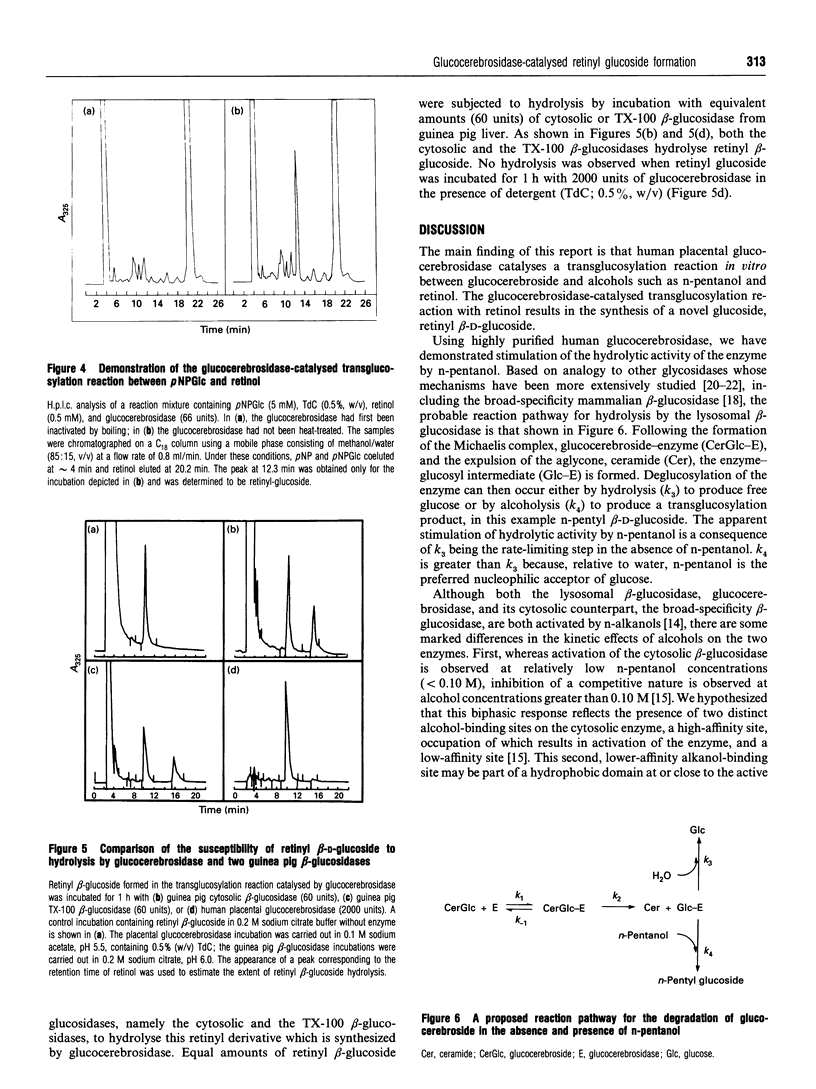
The basal activity of human placental glucocerebrosidase is elevated 16-fold by n-pentanol when assayed using p-nitrophenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (pNPGlc) as the beta-glucosidase substrate. This enhancement of activity is the result of the formation of a transglucosylation product, n-pentyl beta-D-glucoside, in rate-determining competition with the hydrolytic reaction. The transglucosylation product accounts for approximately 80% of the reaction product generated in the presence of n-pentanol (0.18 M) when either glucocerebroside or pNPGlc was used as the substrate. This stimulatory effect can be increased an additional 3-fold by the inclusion of phosphatidylserine (20 micrograms/ml) or sodium taurodeoxycholate (0.3%, w/v) in the incubation medium. In the presence of retinol, glucocerebrosidase also catalyses the synthesis of a novel lipid glucoside, retinyl glucoside, when either glucocerebroside or pNPGlc serves as the substrate. The reaction product was identified as retinyl beta-D-glucoside, based on its susceptibility to hydrolysis by almond beta-D-glucosidase and the subsequent release of equimolar amounts of retinol and glucose. The rate of retinyl-beta-glucoside formation is dependent on the concentration of retinol in the incubation medium, reaching saturation at approximately 0.3 mM retinol. Retinyl beta-D-glucoside is a substrate for two broad-specificity mammalian beta-glucosidases, namely the cytosolic and membrane-associated beta-glucosidases of guinea pig liver. However, retinyl beta-D-glucoside is not hydrolysed by placental glucocerebrosidase. These data indicate that the glucocerebrosidase-catalysed transfer of glucose from glucocerebroside to natural endogenous lipid alcohols, followed by the action of a broad-specificity beta-glucosidase on the transglucosylation product, could provide mammals with an alternative pathway for the breakdown of glucocerebroside to glucose and ceramide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu A., Glew R. H. Characterization of the phospholipid requirement of a rat liver beta-glucosidase. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):515–524. doi: 10.1042/bj2240515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiao Y. B., Hoyson G. M., Peters S. P., Lee R. E., Diven W., Murphy J. V., Glew R. H. Multiple glycosidase deficiencies in a case of juvenile (type 3) Gaucher disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L. B., Coyle P. J., Chiao Y. B., Glew R. H., Labow R. S. Purification and characterization of a cytosolic broad specificity beta-glucosidase from human liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13004–13013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth G. W., Romero K. M., Alverson J., VanderJagt D. J., Glew R. H. Variable expression of leukocyte cytosolic broad-specificity beta-glucosidase activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1993 Jul 16;216(1-2):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(93)90135-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Basu A., LaMarco K. L., Prence E. M. Mammalian glucocerebrosidase: implications for Gaucher's disease. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):5–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Peters S. P., Christopher A. R. Isolation and characterization of beta-glucosidase from the cytosol of rat kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 23;422(1):179–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalan V., Glew R. H., Libell D. P., DePetro J. J. The dual effects of alcohols on the kinetic properties of guinea pig liver cytosolic beta-glucosidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15418–15422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalan V., Vander Jagt D. J., Libell D. P., Glew R. H. Transglucosylation as a probe of the mechanism of action of mammalian cytosolic beta-glucosidase. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9629–9638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski G. A., Gatt S., Horowitz M. Acid beta-glucosidase: enzymology and molecular biology of Gaucher disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(6):385–414. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K. L., Glew R. H. Hydrolysis of a naturally occurring beta-glucoside by a broad-specificity beta-glucosidase from liver. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):469–476. doi: 10.1042/bj2370469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Bieberich E. Isolation of a cytosolic beta-glucosidase from calf liver and characterization of its active site with alkyl glucosides and basic glycosyl derivatives. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90466-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto S., Kishimoto Y., Tomich J., Weiler S., Ohashi T., Barranger J. A., Kretz K. A., O'Brien J. S. Interaction of saposins, acidic lipids, and glucosylceramidase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1933–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Raghavan S. S., Kanfer J. N. Hydrolytic and transglucolytic activities of a partially purified calf brain beta-glucosidase. J Neurochem. 1976 Oct;27(4):943–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb05159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockerman P. A. Identity of beta-glucosidase, beta-xylosidase and one of the beta-galactosidase activities in human liver when assayed with 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glycosides studies in cases of Gaucher's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 6;165(1):59–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi T., Hong C. M., Weiler S., Tomich J. M., Aerts J. M., Tager J. M., Barranger J. A. Characterization of human glucocerebrosidase from different mutant alleles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3661–3667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr J. W., Keranen L. M., Newton A. C. Reversible exposure of the pseudosubstrate domain of protein kinase C by phosphatidylserine and diacylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15263–15266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owada M., Sakiyama T., Kitagawa T. Neuropathic Gaucher's disease with normal 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-glucosidase activity in the liver. Pediatr Res. 1977 May;11(5):641–646. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197705000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., Lee R. E., Glew R. H. A microassay for Gaucher's disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 May 1;60(3):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pócsi I., Kiss L. Kinetic studies on the broad-specificity beta-D-glucosidase from pig kidney. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):139–146. doi: 10.1042/bj2560139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. M., Wilson I. B. A common intermediate in the hydrolysis of -galactosides by -galactosidase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):1061–1064. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezurike G. M. Kinetic properties of -glucosidase from Botryodiplodia theobromae Pat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;250(1):182–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Groen G., Wouters-Leysen J., Yde M., De Bruyne C. K. Effects of alcohols on beta-galactosidase-catalyzed hydrolysis of n-alkyl-beta-D-galactopyranosides. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):122–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Weely S., Brandsma M., Strijland A., Tager J. M., Aerts J. M. Demonstration of the existence of a second, non-lysosomal glucocerebrosidase that is not deficient in Gaucher disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 24;1181(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(93)90090-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


