Fig. 1.
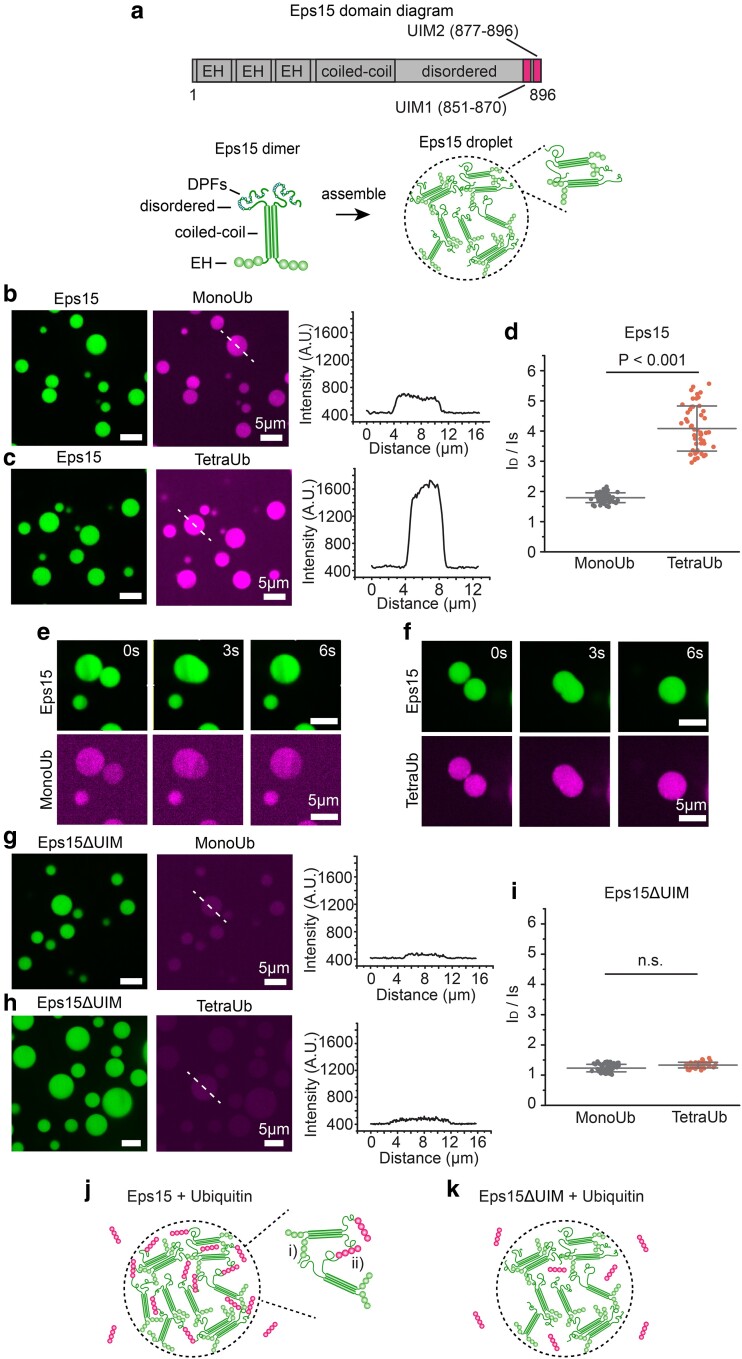
Polyubiquitin partitions strongly into liquid-like droplets of Eps15. a) Top: Schematic of Eps15 functional domains. Eps15 consists of three EH domains at its N terminus followed by a coiled-coil domain and a long disordered region containing two UIMs at the C-terminal end. Bottom: cartoons depict domain organization of Eps15 in dimeric form. DPF motifs are interspersed throughout the disordered region, which can bind the EH domains and allow itself to assemble into liquid-like droplets. b, c) Eps15 (7 μM) droplets incubated with 1 μM MonoUb, and 0.25 μM K63 linkage TetraUb, respectively. Plots on the right depict intensity profile of ubiquitin channel along the dashed line shown in the corresponding images. d) The distribution of the ubiquitin intensity ratio between the intensity inside the droplets (ID) and the solution (IS). In total, 50 droplets were analyzed under each condition. e, f) Representative time course of fusion events between droplets containing Eps15 and MonoUb (e) and droplets containing Eps15 and TetraUb (f). g–i) Same with (b–d) except that droplets were formed with Eps15 mutant, Eps15ΔUIM, with the depletion of the two UIMs (aa 851–896). j, k) Pictorial representation of ubiquitin binding and partitioning into Eps15 droplets through interaction with UIMs at the C terminus of Eps15 (j) and deletion of UIMs impairs ubiquitin partitioning into Eps15 droplets (k). Inset in j shows the two types of interactions in Eps15-polyubiquitin network: (i) DPF motif interacting with EH domain, and (ii) polyubiquitin interacting with UIM domains. All droplet experiments were performed in 20 mM Tris–HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM TCEP, 1 mM EDTA, and 1 mM EGTA at pH 7.5 with 3% w/v PEG8000. Error bars are standard deviation. Statistical significance was tested using an unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test. All scale bars equal 5 μm.