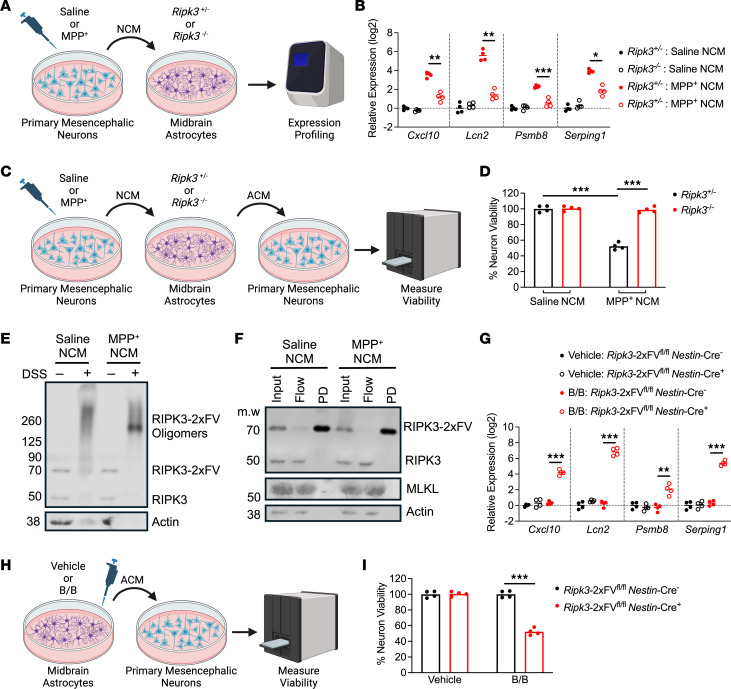
Figure 6. RIPK3 activation is sufficient to induce astrocyte-mediated killing of primary neurons.
(A) Schematic of experimental design for DAMP transfer experiments. (B) qRT-PCR profiling of indicated genes in astrocytes treated for 24 hours with clarified NCM supernatants. (C) Schematic of experimental design for neurotoxicity assay. (D) CellTiter-Glo analysis of neuron viability 24 hours following treatment with ACM derived from indicated conditions. (E and F) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in astrocytes expressing FLAG-tagged RIPK3 following 24 hours of treatment with NCM and DSS cross-linking (E) or bead-mediated FLAG pulldown (F). (G) qRT-PCR profiling of indicated genes in astrocytes of indicated genotypes treated for 24 hours with B/B homodimerizer. (H) Schematic of experimental design for neurotoxicity assay in which astrocytes expressing (or not) RIPK3-2xFV were treated with B/B homodimerizer or vehicle solution for 24 hours. Astrocytes were then washed and media replaced for another 24 hours. ACM was then transferred to WT primary neurons for cell viability measurement. (I) CellTiter-Glo analysis of viability in WT neurons 24 hours following treatment with ACM derived from indicated conditions. n = 4 cultures/per group in all panels. Data are represented as mean values with scatterplots depicting individual biological replicate values. All comparisons via 2-way ANOVA with Holm-Šídák multiple-comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. A, C, and H were created with Biorender.com.