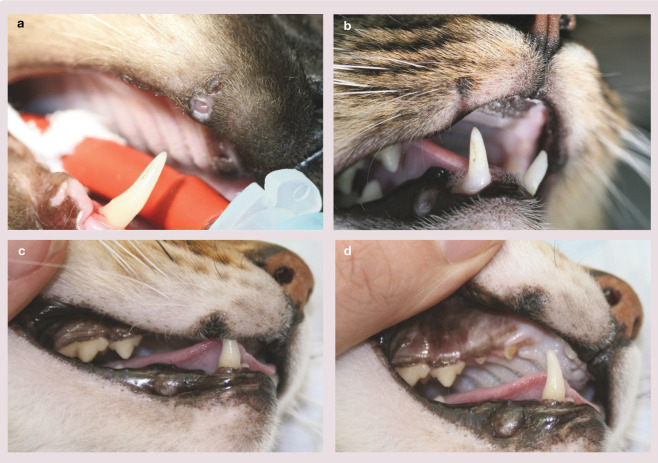
Figure 24.
Canine malocclusion. (a) Ulceration resulting from penetration of the mandibular canine tooth (404) following extraction of the maxillary canine (104). (b) Keratinised area from a chronic lesion. Many of these cases do not need treatment if the cat seems comfortable. (c,d) Lip ulceration secondary to loss of the maxillary crown. Previously this trauma was only described post-extraction due to loss of the buccal bone plate; however, it is actually the crown of the maxillary canine that prevents contact of the mandibular canine and upper lip. Photograph (d) shows the maxillary canine (104) fractured at the gingival margin