Figure 2.
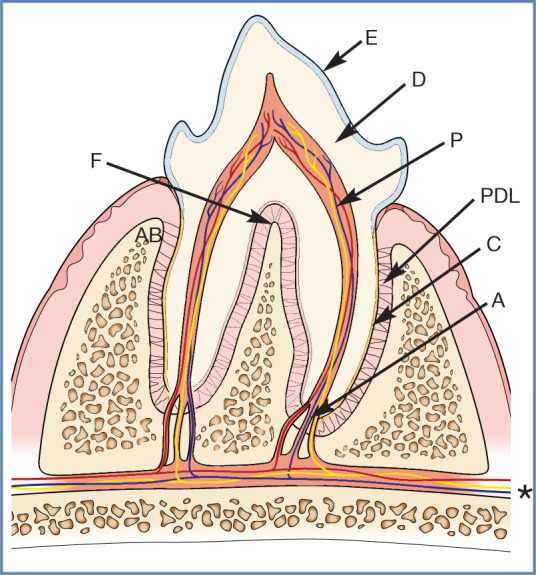
Basic tooth anatomy. The crown of the tooth is covered in enamel (E), and the roots are covered in cementum (C). Dentine (D) comprises the majority of the hard tissue of the tooth. Within the tooth is the pulp (P). This is a soft tissue composed of arteries, veins and nerves, which enter through the apex of the root (A) (these are branches from the maxillary and mandibular artery, vein and nerves [*]), as well as lymphatics, fibroblasts, odontoblasts and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells. Within the crown the pulp space is termed the pulp chamber and within the root the root canal. The periodontal ligament (PDL) anchors the tooth within the alvelous by attaching to the cementum and alveolar bone (AB). The furcation (F) is where the roots divide and, in health, this area is filled with alveolar bone
