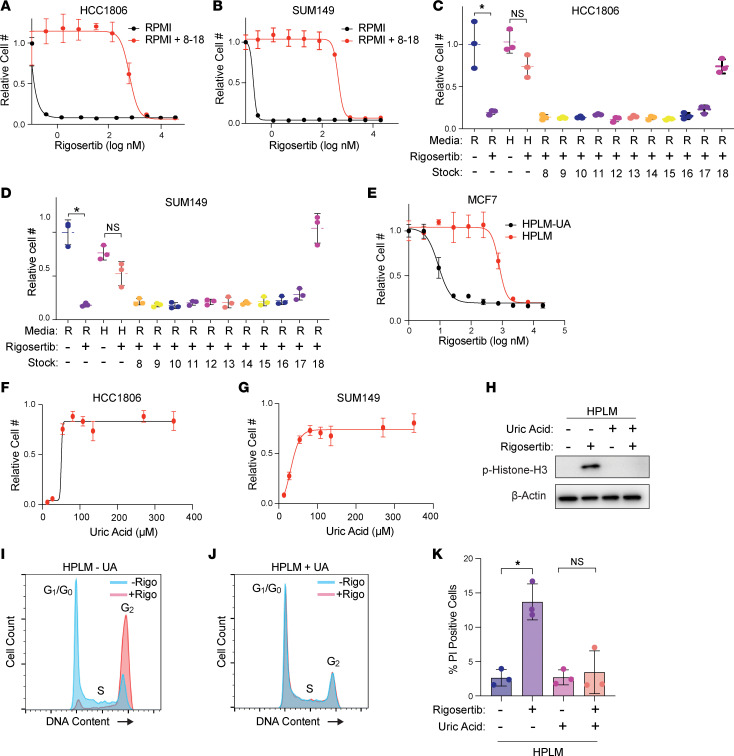
Figure 3. Uric acid prevents the activity of rigosertib.
(A and B) Dose-response curves of HCC1806 (A) and SUM149 (B) cells treated with rigosertib in RPMI versus RPMI + HPLM stocks 8–18. (C and D) Cell growth assays of HCC1806 (C) and SUM149 (D) cells treated with 80 nM rigosertib in the presence of individual HPLM stocks 8–18. R, RPMI; H, HPLM. (E) Dose-response curve of MCF7 cells treated with rigosertib in HPLM versus HPLM – UA. UA, uric acid. (F and G) Dose-response curves of uric acid on HCC1806 (F) and SUM149 (G) cells treated with 80 nM rigosertib. (H) Representative Western blot of phosphorylated histone H3 in HCC1806 cells treated with 150 nM rigosertib in HPLM versus HPLM – UA. (I and J) Cell cycle analysis of HCC1806 cells treated with 150 nM commercial-grade rigosertib in HPLM (I) and HPLM – UA (J). (K) Cell death analysis of HCC1806 cells treated with 200 nM commercial-grade rigosertib in HPLM and HPLM – UA. For all panels, data are represented as mean ± SD of triplicate samples. * indicates P < 0.05 by unpaired 2-tailed t test.