Figure 3.
mAbs from natural infection primarily target non-neutralizing RH5 epitopes
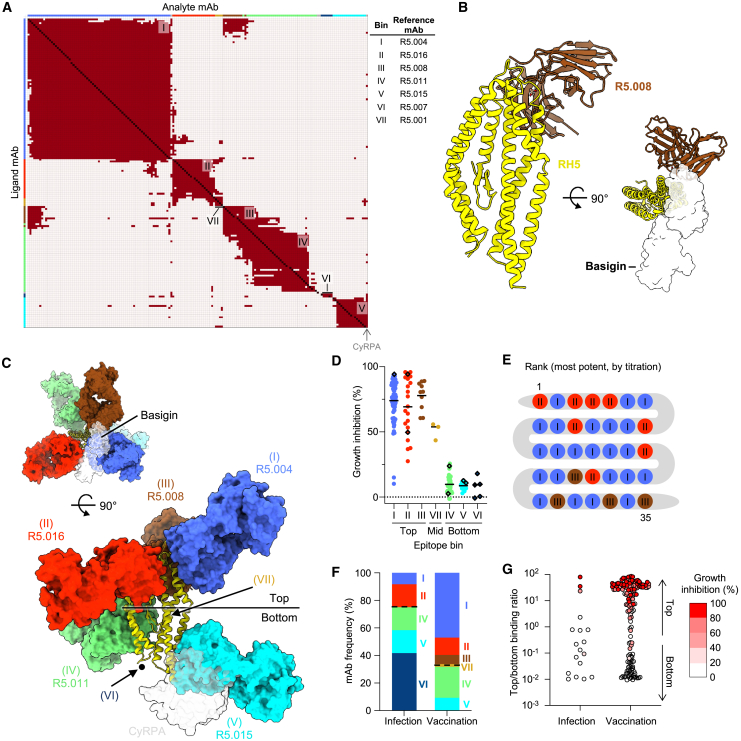
(A) Heatmap showing competition of mAbs targeting RH5. Red squares signify competition between the corresponding analyte and ligand mAb, while cream squares indicate no competition. The colors at the edges are those of the combined bins I–VII (e.g., bin I is formed from Ia–Ic). 13/22 infection-derived mAbs and 153/164 vaccine-derived mAbs were mappable in this assay; the remaining mAbs were incompatible with the workflow, e.g., due to acid sensitivity.
(B) Crystal structure of RH5 (yellow) bound to the scFv of R5.008 (brown), each shown in cartoon. R5.008 competes with the binding of basigin (transparent white surface, PDB: 4U0Q) to RH5.
(C) Neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies target the top and bottom of RH5, respectively. Representative antibody structures for each bin (I = R5.004, PDB: 6RCU; II = R5.016, PDB: 6RCV; III = R5.008; IV = R5.011, PDB: 6RCV; V = R5.015, PDB: 7PHU) are shown in surface representation on RH5 in cartoon. R5.008 is modeled as a Fab fragment for illustrative purposes. The binding locations of basigin (PDB: 4U0Q) and CyRPA (PDB: 8CDD) are shown as transparent surfaces in the top and side views, respectively, and the black dot indicates the location of the internal disordered loop of RH5. The approximate locations of bin VI (based on binding to the intrinsic loop) and bin VII (based on partial overlap with bins II and V) are shown by arrows.
(D) Growth inhibition of mAbs, subdivided by major epitope bin. Bars show mean values. Infection-derived mAbs are shown as diamonds.
(E) Epitope bins of 35 most potent RH5-specific mAbs, as determined by GIA titration.
(F) Frequency of infection- and vaccination-derived mAbs in each RH5 epitope bin. The dotted lines separate bins at the top and bottom of RH5.
(G) mAbs scored by binding proximity to the top of RH5, based on binding to RH5 with bins I–III pre-blocked versus bins IV–VI pre-blocked. Data points are geometric means from two independent experiments. Points are color-coded by GIA score at 1 mg/mL.
See also Figures S2–S4.