Figure 2.
Mrc1 maintains heterochromatin independently of its functions in genome stability and origin regulation
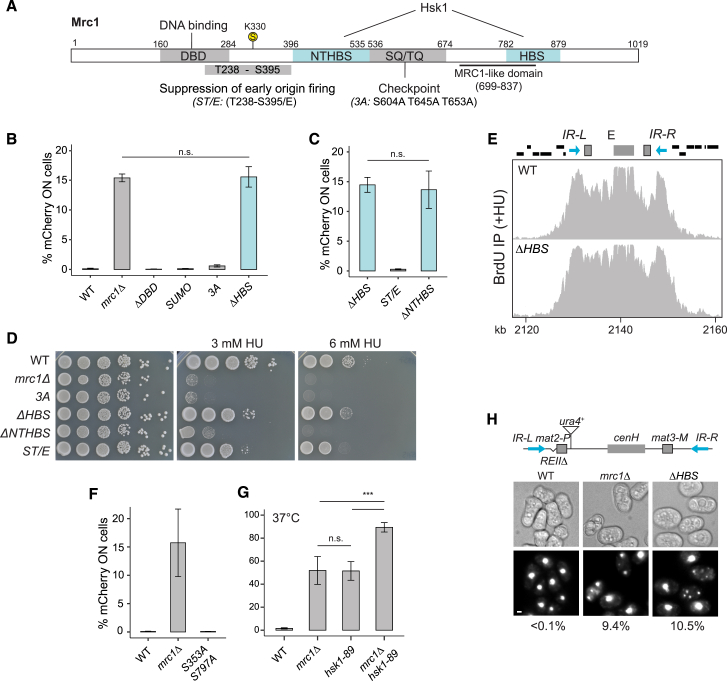
(A) Mrc1 protein with annotated domains and residues. MRC1-like domain refers to the most conserved portion of Mrc1, Pfam domain PF09444.
(B and C) Cells expressing mCherry (n = 6). (B) [ANOVA, F = 654, p = 2.22 × 10−16]; (C) [ANOVA, F = 99, p = 2.13 × 10−9]. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(D) Checkpoint proficiency of mrc1 mutants. 10-fold serial dilutions of cell suspensions were spotted onto HU-containing YES plates and incubated at 33°C for 4 days.
(E) BrdU incorporation profiles in the mating-type region in cells released into S phase in the presence of HU.
(F and G) Cells expressing mCherry (F, n = 3; G, n = 6). (G) Cells were propagated at the permissive temperature for hsk1-89, 37°C, which inherently weakens heterochromatin seen by slight loss of mCherry silencing even in WT cells. [ANOVA, F = 135, p = 1.88 × 10−13]. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(H) Haploid meioses in mrc1Δ and mrc1ΔHBS mutants lacking the REII silencing element visualized by bright field imaging and Hoechst staining of cells propagated on MSA sporulation medium. Scale bar: 1 μm.
See also Figure S1.