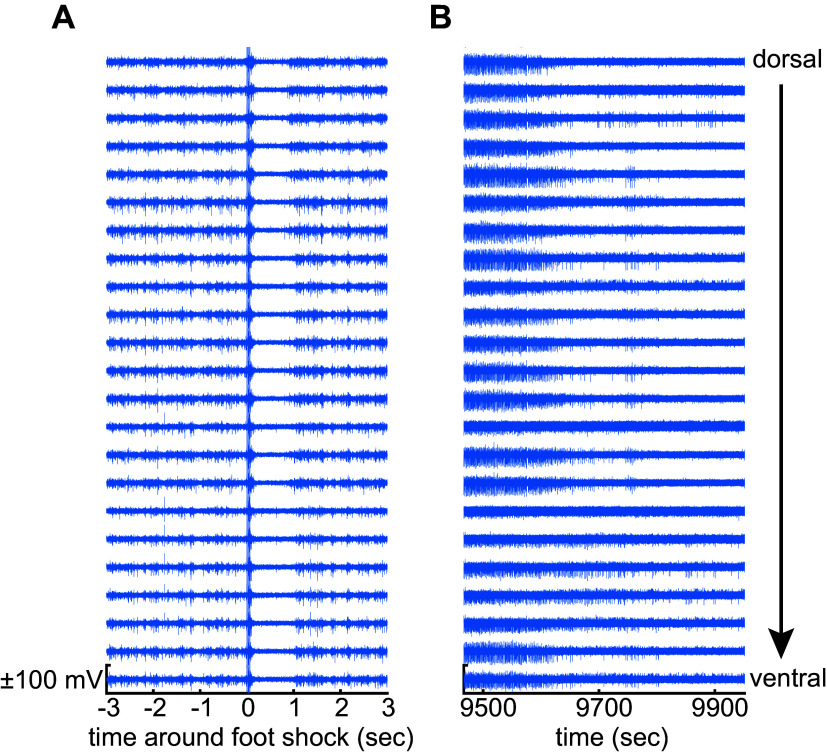
Figure 1.
Feedback inhibition distinguishes locus coeruleus (LC) neurons from non-LC neurons. A: the highpass (500 Hz) filtered signal recorded on a 23-electrode linear array in a ±3-s window around a 5.0 mA foot shock in the urethane-anesthetized rat. Increased spiking after the stimulus releases norepinephrine (NE) locally, which causes feedback inhibition via NE binding to the a2-adrenergic receptor. Data from one example recording (N = 1). B: spiking on the same electrodes after clonidine injection (50 µg/kg ip). Clonidine was injected at the start of the recording trace. Data from one example recording (N = 1).