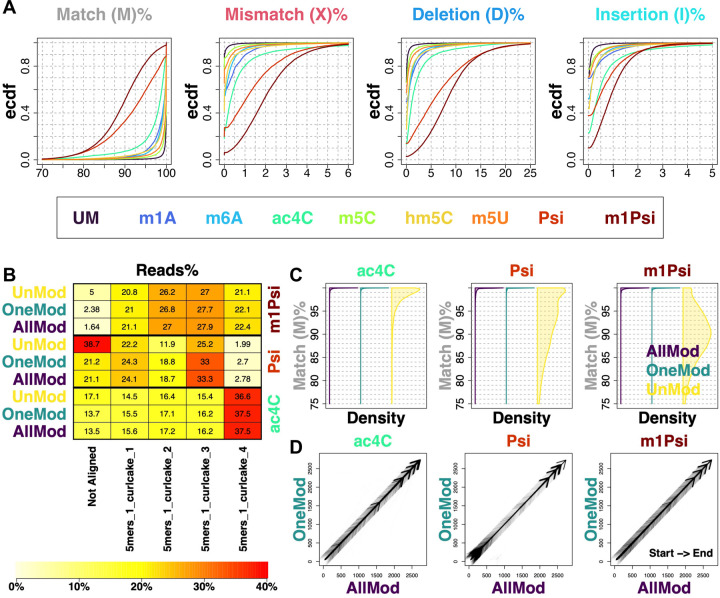
Figure 2. Basecallers trained with diverse known modifications gain the capability to basecall novel modifications.
(A) Performance of the basecaller trained only by the unmodified data on all the read groups. Basecalling performance was assessed with the per-read CIGAR alignment fraction, including match (M), mismatch (X), deletion (D) and insertion (I). UM and acronyms stand for unmodified and modified RNA oligo categories, respectively. Ecdf denotes the empirical cumulative distribution function. Performance of basecallers trained by combining all the oligo groups except for ac4C, Psi or m1Psi was quantified. Specifically, the mappability (B) and per-read CIGAR match fraction (C) were used as quantification metrics. AllMod, the basecaller trained by all the modifications except for the one to be basecalled; OneMod, the basecaller trained with only the modification to be basecalled; UnMod, the basecaller trained by only unmodified reads. (D) Alignment position comparison between “AllMod” and “OneMod”. Start and End denote the alignment direction.