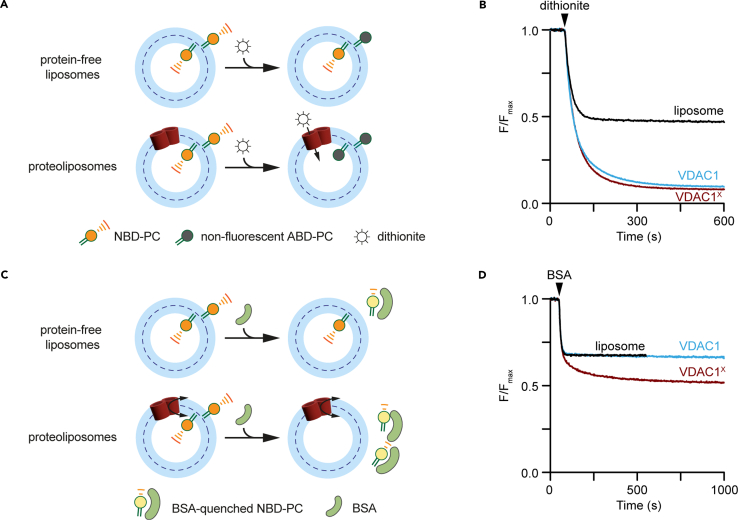
Figure 10.
Crosslinked VDAC1 scrambles phospholipids
(A) VDAC1 channel activity is assayed using the membrane-impermeant reductant dithionite. In protein-free liposomes, dithionite bleaches approximately 50% of NBD-PC fluorescence, corresponding to the phospholipids residing in the outer leaflet. In liposomes reconstituted with VDAC1, dithionite can enter the vesicles and bleach nearly 100% of NBD-PC fluorescence.
(B) Time-course of NBD-PC fluorescence normalized to the average initial signal in liposomes and proteoliposomes containing crosslinked (VDAC1X) and mock-treated (VDAC1) hVDAC1. Vertical arrowhead indicates dithionite addition.
(C) VDAC1 scramblase activity is assayed using BSA which, in contrast to dithionite, is too large to diffuse through the VDAC1 channel. BSA extracts NBD-PC from the outer leaflet and quenches its fluorescence by ∼60%, resulting in ∼30% fluorescence reduction in liposomes and ∼60 fluorescence reduction in proteoliposomes containing crosslinked VDAC1.
(D) Time-course of NBD-PC fluorescence normalized to the average initial signal in liposomes and proteoliposomes containing crosslinked (VDAC1X) and mock-treated (VDAC1) hVDAC1. Vertical arrowhead indicates BSA addition. Liposome and VDAC1 traces overlap extensively; the liposome trace has been terminated at 500 s to facilitate visualization of the VDAC1 trace.