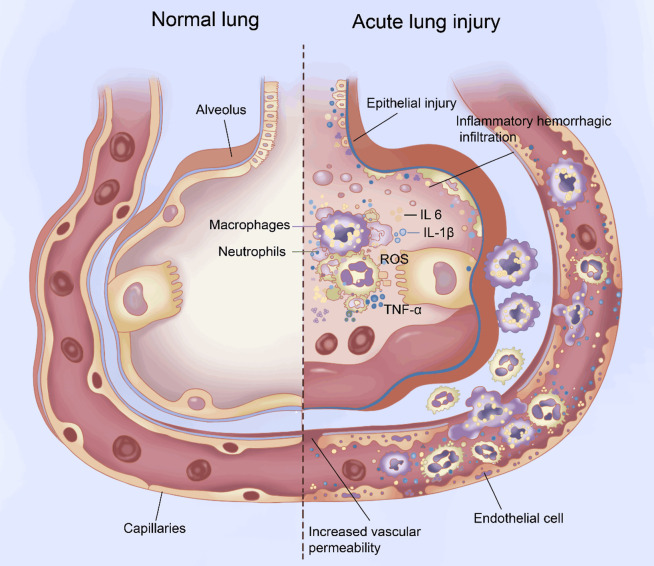
Figure 1.
Pathophysiologic changes during acute lung injury (ALI). Changes involve oxidative stress due to reactive oxygen species (ROS); leukocyte activation; excessive and uncontrolled inflammatory responses mediated by interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α; and injury of the pulmonary epithelium and vascular endothelium.