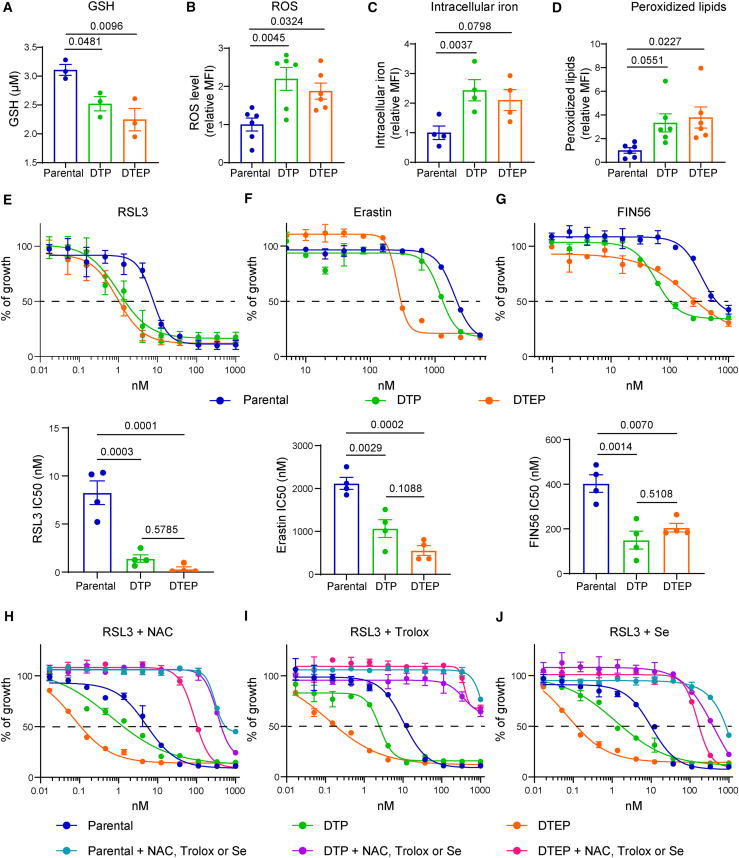
Figure 3.
DTP and DTEP HCC364 cells are hypersensitive to ferroptosis induction in vitro
(A) Intracellular GSH concentration in parental, DTP, and DTEP HCC364 cells. n = 3 biological replicates.
(B) ROS level in parental, DTP, and DTEP HCC364 cells. n = 6 biological replicates.
(C) Iron level in parental, DTP, and DTEP HCC364 cells. n = 4 biological replicates.
(D) Peroxidized lipids content in parental, DTP, and DTEP HCC364 cells. n = 6 biological replicates.
(E–G) Cell viability assessment by MTT assay of parental, DTP, and DTEP HCC364 cells treated with serial dilutions of RSL3 (E), erastin (F), or FIN56 (G) for 72 h (upper panel). IC50 values (lower panel) are represented for each condition. n = 4 biological replicates.
(H–J) Cell viability assessment by MTT assay of parental, DTP, and DTEP HCC364 cells treated with serial dilutions of RSL3 in the presence of 2.5 mM N-acetylcysteine (NAC, H), 10 μM Trolox (I), or 200 nM selenium (Se, J) for 72 h n = 3 biological replicates. All data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test and are shown as the mean values ± SEM. See also Figures S2–S4 and S10.