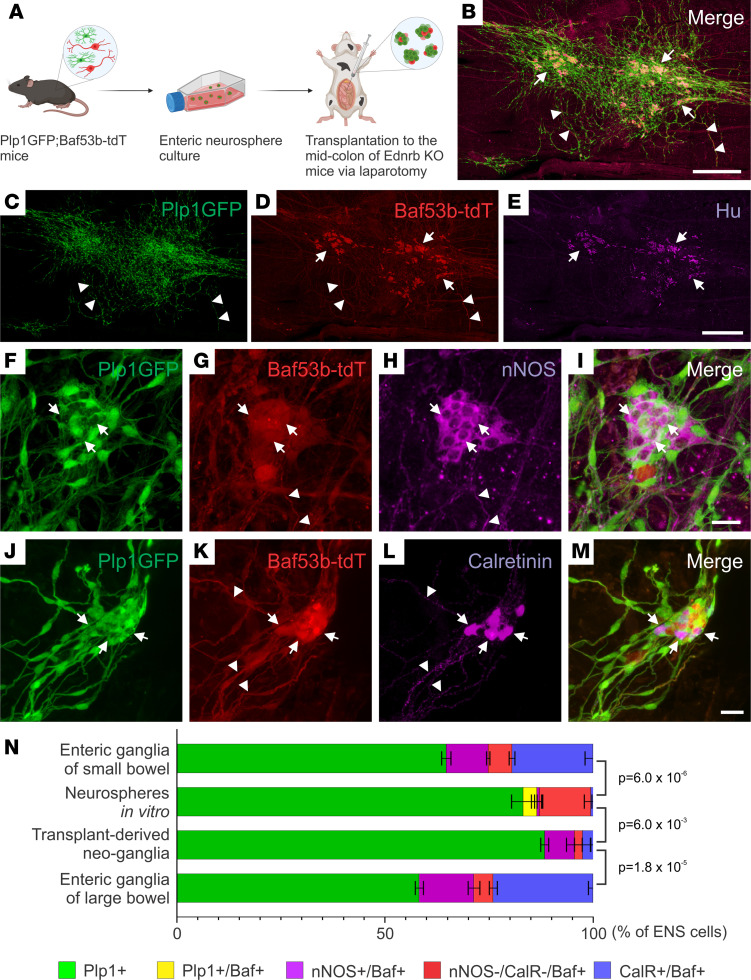
Figure 5. ENSCs transplanted into Ednrb-KO mice via laparotomy formed neo-ganglia that contain enteric neuron subtypes.
The experimental design involves isolation of ENSCs from Plp1GFP;Baf53b-tdT mice, expansion as enteric neurospheres, and transplantation into the midcolon of recipient HSCR mice by multiple injections via laparotomy (A). Two weeks following surgery, transplanted cells are present in the aganglionic recipient colon (B). Many cell clusters contain neurons (C–E, arrows), and extensive fiber projections are seen (C and D, arrowheads). Transplanted ENSC-derived neo-ganglia contain nNOS-immunoreactive (F–I, arrows) and calretinin-immunoreactive (J–M, arrows) neurons with fibers (G, H, K, and L, arrowheads). Cell compositions in “Neurospheres in vitro” and “Transplant-derived neo-ganglia” were compared with those in the enteric ganglia of small or large bowel of 1- to 2-month-old WT mice (N). Statistical significance was determined by Fishers’ exact test. Scale bars: 25 μm (F–M) and 500 μm (B–E).