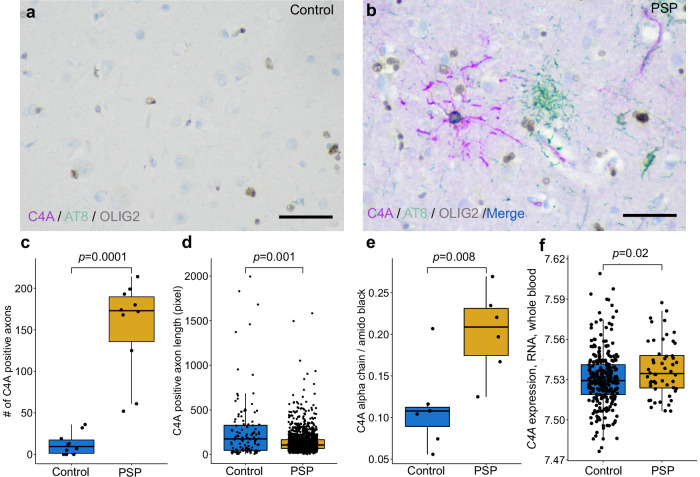
Fig. 7. Elevation of C4A protein in the frontal cortex of human postmortem progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) brain tissue.
a Triple immunohistochemical stains of C4A (magenta), hyperphosphorylated tau (AT8, green), and OLIG2 (brown) show limited C4A and hyperphosphorylated tau staining in controls (b). Staining in PSP demonstrates colocalization of C4A and hyperphosphorylated tau in an OLIG2 positive coiled body (blue and brown). Tufted astrocyte cell bodies (green) and neurofibrillary tangles (not shown) are negative for C4A in PSP. The average number of C4A positive axons per subject (c) was significantly higher in PSP than controls (n = 10 cases and controls, frontal cortex, 5 regions of interest per subject, 1538 observations found in PSP, 124 in controls). Quantification of C4A positive axons revealed significantly shorter (d) axonal length in PSP when compared to controls. e Quantitative immunoblots of the C4A alpha chain showed significantly higher levels in PSP compared to controls (n = 7 cases, 6 controls). f C4A gene expression in whole blood from patients with PSP was significantly higher than controls (n = 51 cases, 281 controls). The scale bar is 50 micrometers.