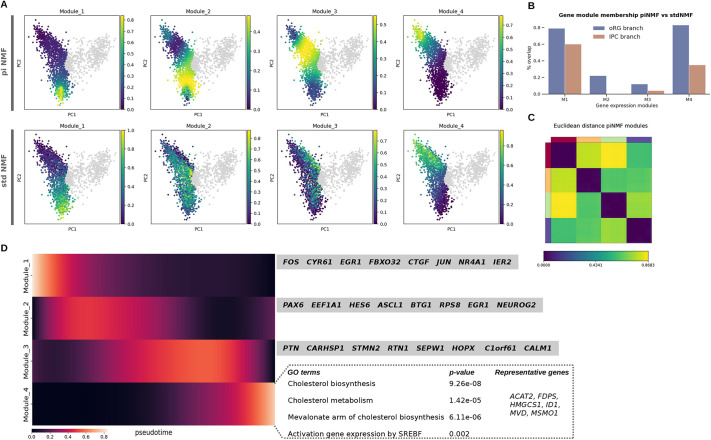
Fig. 2.
Pseudotime-informed non-negative matrix factorization recovers a sequential activation of gene expression programs. (A) Comparatively in PCA plots, piNMF is able to resolve expression programs transiently activated for the lineage branch leading to the outer radial glial cell (oRG) cluster [same for the intermediate progenitor cell (IPC) branch, see Fig. S4], whereas stdNMF does not recover such clear patterns from the data. The scale 0 to 1 denotes activation of each gene expression program in each cell. (B) Genes assigned to modules at the extreme of the lineage tree [ventricular radial glia (vRG) and either oRG or IPC] are shared in higher percentage when compared with modules 2 and 3, confirming that the main differences among non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) algorithms pertain to the transient activation of expression programs along the tree. (C) The high values on the Euclidean distance among the four gene expression programs supports, along with the stability and error measures (see Fig. S4), the factorization rank selection. (D) Heatmap depicting the sequential activation of expression programs in the radial glia branch, with marker genes for each module and, for module 4, representative GO terms highlighted in the main text.