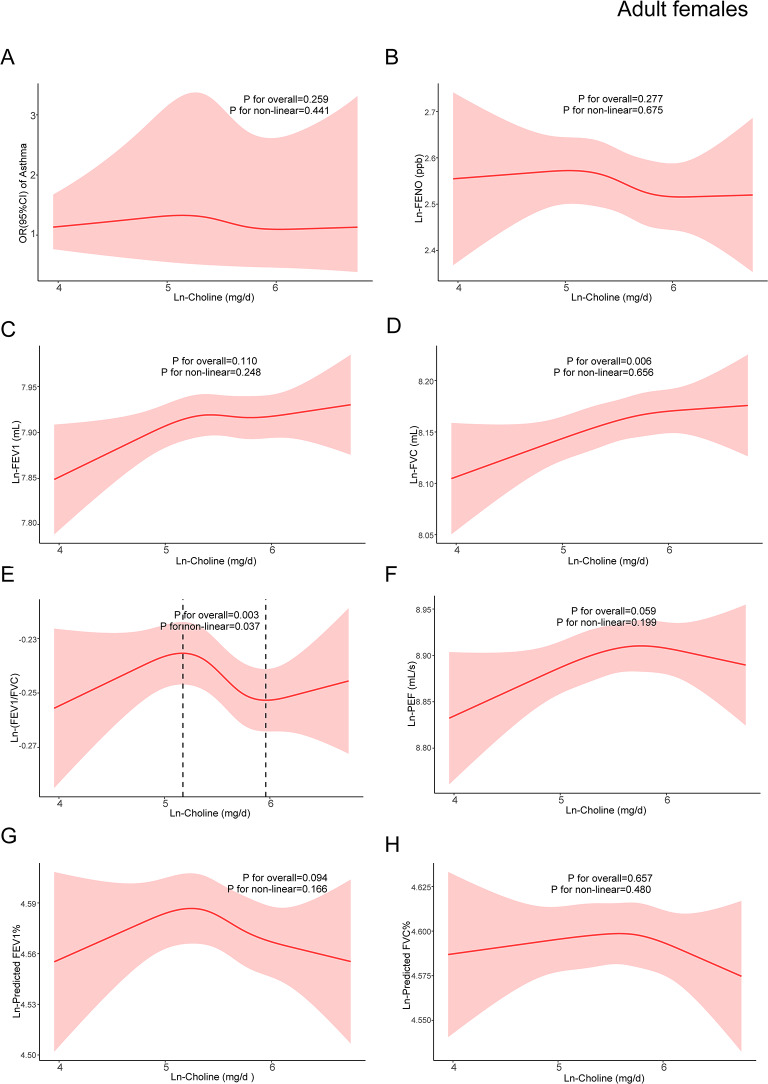
Fig. 3.
The dose-response relationship between dietary choline intake and asthma, pulmonary inflammation and lung function indicators in adult females. The red line represented the estimated β or OR and the red shading around it represented its 95% confidence intervals. OR: odds ratio; FENO: fractional exhaled nitric oxide; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in one second; FVC: forced vital capacity; PEF: peak expiratory flow rate. (A)The relationship between ln-choline and asthma in adult females. (B) The relationship between ln-choline and ln-FENO in adult females. (C) The relationship between ln-choline and ln-FEV1 in adult females. (D) The relationship between ln-choline and ln-FVC in adult females. (E) The relationship between ln-choline and ln-(FEV1/FVC) in adult females. (F) The relationship between ln-choline and ln-PEF in adult females. (G) The relationship between ln-choline and ln-predicted FEV1% in adult females. (H) The relationship between ln-choline and ln-predicted FVC% in adult females. Adjusted for age, race, marital status, education level, PIR, obesity status, physical activity, blood cotinine, family history of asthma, menopausal status, folate DFE, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, history of diabetes and hypertension