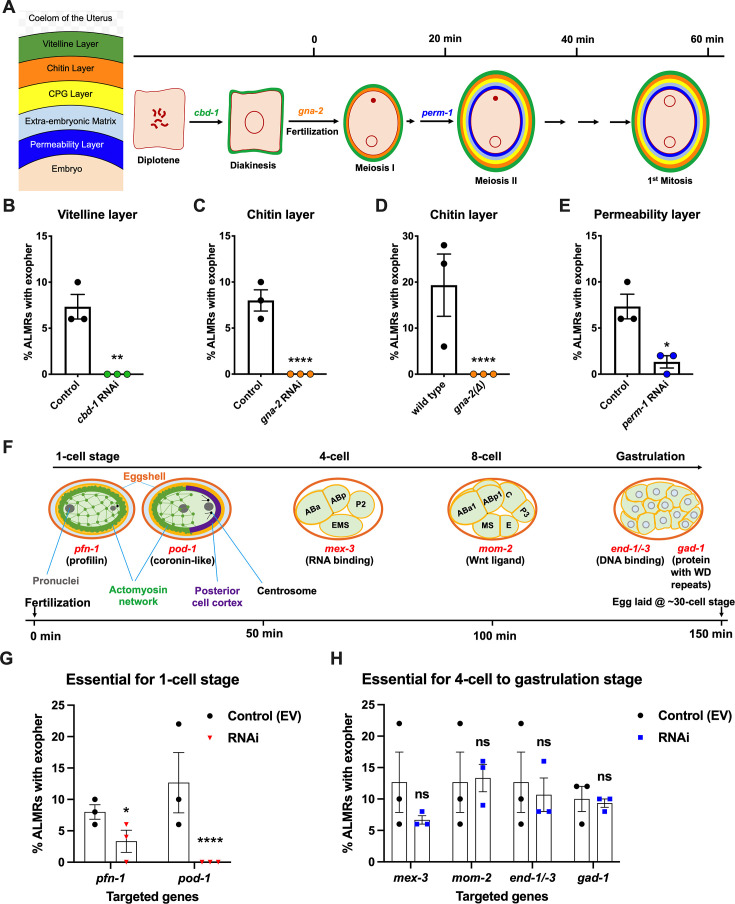
Figure 2. Events required for adult day 2 (Ad2) elevation of exopher production occur during the earliest stages consequent to fertilization and are largely completed by the 4-cell stage.
(A) Diagram of eggshell layers, post-fertilization timeline for layer formation, and indication of steps at which RNAi disrupts eggshell biogenesis. The formation of the multilayered eggshell is accomplished via a hierarchical assembly process from outside to inside, with outer layers required for later formation of inner layers. The outmost vitelline layer assembles in part prior to fertilization, dependent on chitin-binding domain protein (CBD-1) González et al., 2018. The next eggshell layer is made up of chitin, which confers eggshell stiffness and requires the gna-2-encoded enzyme glucosamine-6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase (GNPNAT1) for precursor biosynthesis (Johnston et al., 2006). The innermost lipid layer of eggshell is called the permeability layer, which is lipid-rich and is needed to maintain osmotic integrity of the embryo. PERM-1 (Olson et al., 2012) (among others, including FASN-1 [Rappleye et al., 2003], POD-1 [Rappleye et al., 1999], and EMB-8 [Benenati et al., 2009]) is required for permeability barrier formation (Stein and Golden, 2018; Johnston and Dennis, 2012). Note that eggshell biogenesis is critical for polyspermy barrier, spermathecal exit, meiotic chromosome segregation, polar body extrusion, AP polarization and internalization of membrane and cytoplasmic proteins, and correct first cell divisions (Johnston and Dennis, 2012), so genetic separation of eggshell malformation from the earliest embryonic formation is not possible. (B) cbd-1, a gene encoding an essential component of the eggshell vitelline layer, is critical for Ad2 exopher elevation. Exopher scores in Ad2 animals (strain ZB4757: bzIs166[Pmec-4::mCherry] II) that were treated with RNAi against cbd-1, total of three trials (50 hermaphrodites per trial), **p<0.01 in Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test, as compared to the empty vector (EV) control. (C) gna-2, a gene required for chitin precursor biosynthesis and chitin layer formation, is critical for Ad2 exopher elevation. (C) Exopher scores in Ad2 animals treated from the L1 stage with RNAi against gna-2. The gna-2 gene encodes enzyme glucosamine-6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase (GNPNAT1) required for chitin precursor biosynthesis. (D) Exopher scores in Ad2 animals harboring a null mutation in the essential gna-2 gene. gna(∆) homozygous null worms are GFP negative progeny of stain ZB4941: bzIs166[Pmec-4::mCherry]; gna-2(gk308) I/hT2 [bli-4(e937) let-?(q782)] qIs48[Pmyo-2::GFP; Ppes-10::GFP; Pges-1::GFP] (I;III). Data represent a total of three trials (50 hermaphrodites per trial), **** p<0.0001 in Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test, as compared to wild-type animals. (E) perm-1, a gene required for permeability barrier synthesis, is critical for Ad2 exopher elevation. Exopher scores in Ad2 animals treated with RNAi against perm-1, which encodes a sugar modification enzyme that acts in the synthesis of CDP-ascarylose. Data represent a total of 3 trials (50 hermaphrodites per trial), *p<0.05 in Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test, as compared to the EV control. Note that previously characterized strong exopher suppressors pod-1, emb-8, and fasn-1 (Melentijevic et al., 2017; Cooper et al., 2021) are also needed for egg shell permeability barrier layer formation (Rappleye et al., 1999; Benenati et al., 2009). (F) Diagram of select genes required for specific stages of embryonic development. pfn-1 RNAi (arrest at the one-cell stage Schonegg et al., 2014; pod-1 RNAi (arrest at the two-cell stage Luke-Glaser et al., 2005; arrest stage phenotype for other genes is not precisely documented, but these genes play significant roles at the indicated stages; images annotated according to WormAtlas (https://doi.org/10.390/wormatlas.4.1). (G) RNAi targeting of early acting embryonic development genes lowers exopher production. Exopher scores from Ad2 animals that were treated with RNAi against genes characterized to be essential for 1-cell to 2-cell stage embryonic development. Total of three trials (50 hermaphrodites per trial). *p<0.05 or ****p<0.0001 in Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test, as compared to the empty vector control. Strong exopher suppressor pod-1 has been previously reported (Melentijevic et al., 2017). We found RNAi directed against gene emb-8 (as early as 2 cell arrest, but arrest at the 1- to 50 cell stage reported [Schierenberg et al., 1980]) to be more variable in outcome (not shown). (H) RNAi targeting of genes that disrupt 4 cell stage and later embryonic development does not alter exopher production levels. Exopher scores in Ad2 animals that were treated with RNAi against genes that are essential for 4 cell to gastrulation stages of embryonic development. Total of three trials (50 hermaphrodites per trial). ns, not significant in Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test, as compared to the empty vector control.