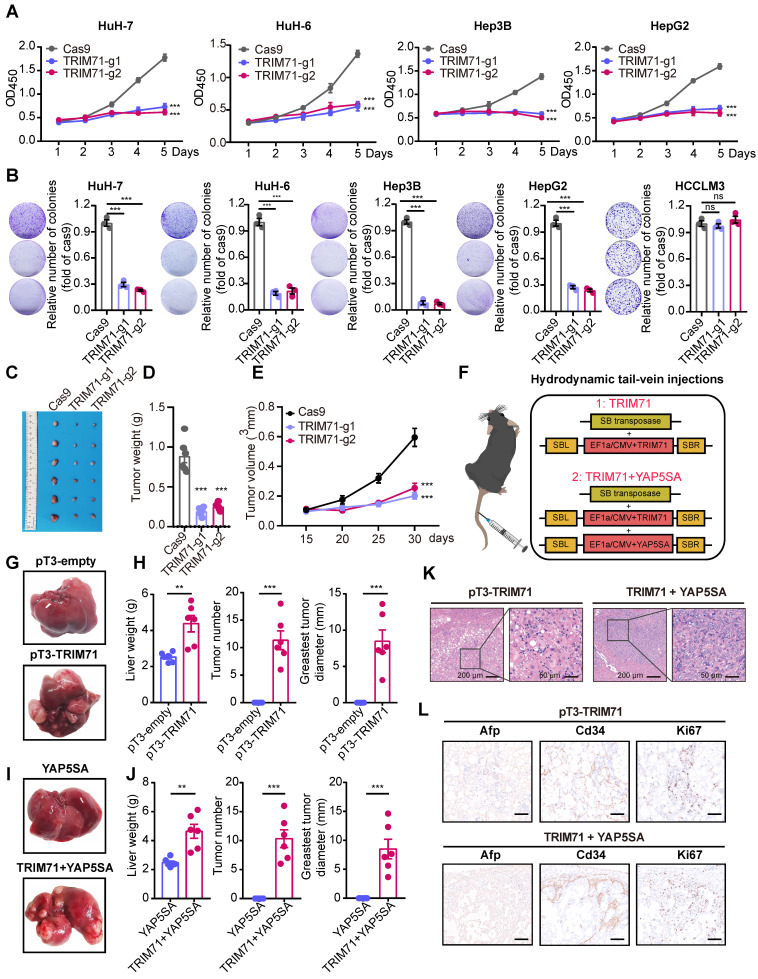
Figure 3.
TRIM71 drives liver cancer initiation and progression. (A) Effects of TRIM71 knockdown on cell proliferation in HuH-7, HuH-6, Hep3B and HepG2 cells infected with sgTRIM71 specific gRNAs and Cas9 lentiviruses and determined by cell-counting kit 8 (CCK-8) assay. (B) Colony formation assays of HuH-7, HuH-6, Hep3B, HepG2 and HCCLM3 cells infected with sgTRIM71 specific gRNAs and Cas9 lentiviruses. (C) Images of the xenograft mouse models implanted with HuH-7 cells with or without TRIM71 knockdown infected with sgTRIM71 specific gRNAs and Cas9 lentiviruses. (D-E) Effects of TRIM71 knockdown on the tumor weight (D) and tumor volume (E) of HuH-7 xenograft tumors. (F) The experimental scheme for the generation of liver tumor mouse models using hydrodynamic tail-vein injection technology. (G) Representative images of tumors dissected from pT3-empty and pT3-TRIM71 liver tumor mouse models. (H) Liver weight, tumor number and greatest tumor diameter in pT3-empty and pT3-TRIM71 liver tumor mouse models. (I) Representative images of tumors dissected from YAP5SA and TRIM71 + YAP5SA liver tumor mouse models. (J) Liver weight, tumor number and greatest tumor diameter of YAP5SA and TRIM71 + YAP5SA liver tumor mouse models. (K) The HE staining in TRIM71 and TRIM71 + YAP5SA liver tumor mouse models. (L) Immunohistochemistry staining showing Afp, Cd34 and Ki67 protein expression in tumor tissues of TRIM71 and TRIM71 + YAP5SA liver tumor mouse models. Values represent the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.