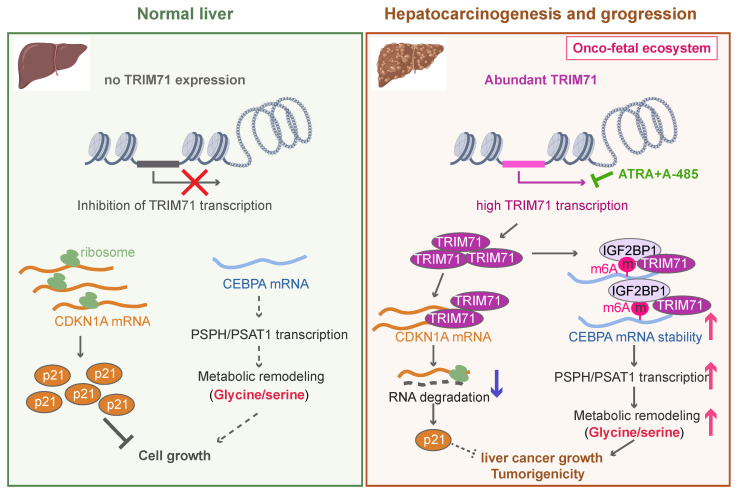
Figure 8.
The working model of TRIM71 in manipulating liver cancer initiation and progression. In normal liver, the transcription of TRIM71 is inhibited, which accompanied by the low CEBPA mRNA levels and high CDKN1A mRNA levels. CDKN1A translates abundant p21 proteins and glycine/serine metabolism is inhibited, resulted in restricted cell growth (Left). In liver cancer, TRIM71 is specifically and highly expressed, and established the oncofetal ecosystem. TRIM71 degradates CDKN1A mRNA to decrease p21 protein. More importantly, TRIM71 forms protein complex with IGF2BP1, which binds to and stabilize CEBPA mRNA levels through m6A dependent manner. High expression of CEBPA remodels glycine/serine metabolism through enhancing PSPH/PSAT1 transcription, and ultimately promotes liver cancer growth and tumorigenicity. Targeting inhibition of TRIM71 using ATRA combined with A-485 may offer potentially therapeutic strategies for liver cancer patients with high TRIM71 levels (Right).