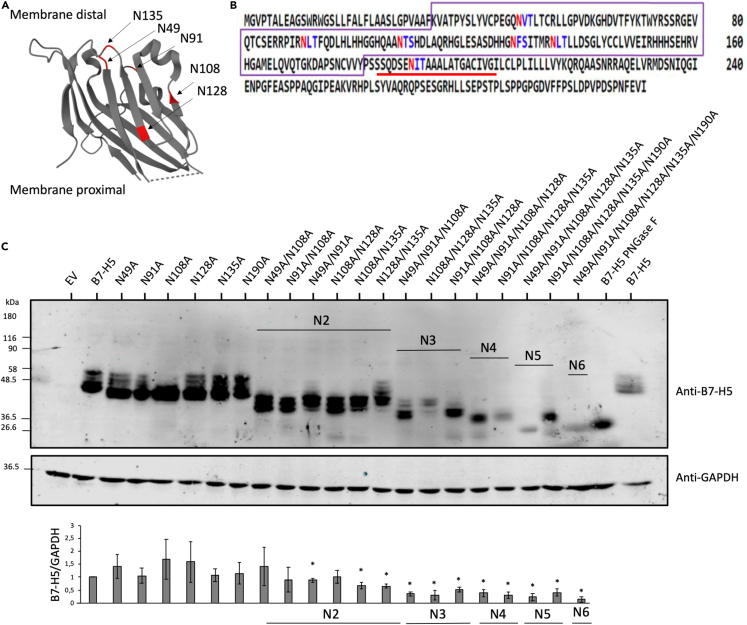
Figure 2.
N-glycosylation sites of B7-H5
(A) Depiction of B7-H5 3D structure and localization of the amino acids targeted by glycosylation in the extracellular region (N49, N91, N108, N128, N135). Extracellular domain of B7-H5 is shown according to accession 6OIL.28 Crystal structure visualization by Protein DataBank. N-glycosylated sites are highlighted in red.
(B) Potential N-glycosylation sites in B7-H5 protein sequences (NP_071436.1). Asn/N that have a high probability of being N-glycosylated are shown in red, whereas Asn/N that have a lower probability of being N-glycosylated are shown in blue. IgV domain is highlighted in a violet box, and transmembrane region is underlined in red.
(C) Western blot of total lysates from HEK293 cells ectopically expressing B7-H5, B7-H5 N49A, N91A, N108A, N128A, N135A, N190A single and multiple mutations (N2-N6), as indicated. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1+/C-DYK empty vector (EV), or with B7-H5 variants. B7-H5 WT lysate was kept untreated or treated with PNGase F, as indicated. Anti-B7-H5 was used for identification of B7-H5 protein and anti-GAPDH was used as a loading control. In the lower panel, quantification of B7-H5/GAPDH is shown from three independent blots, ± SD. Statistically significant results (p < 0.05) are marked with an asterisk.