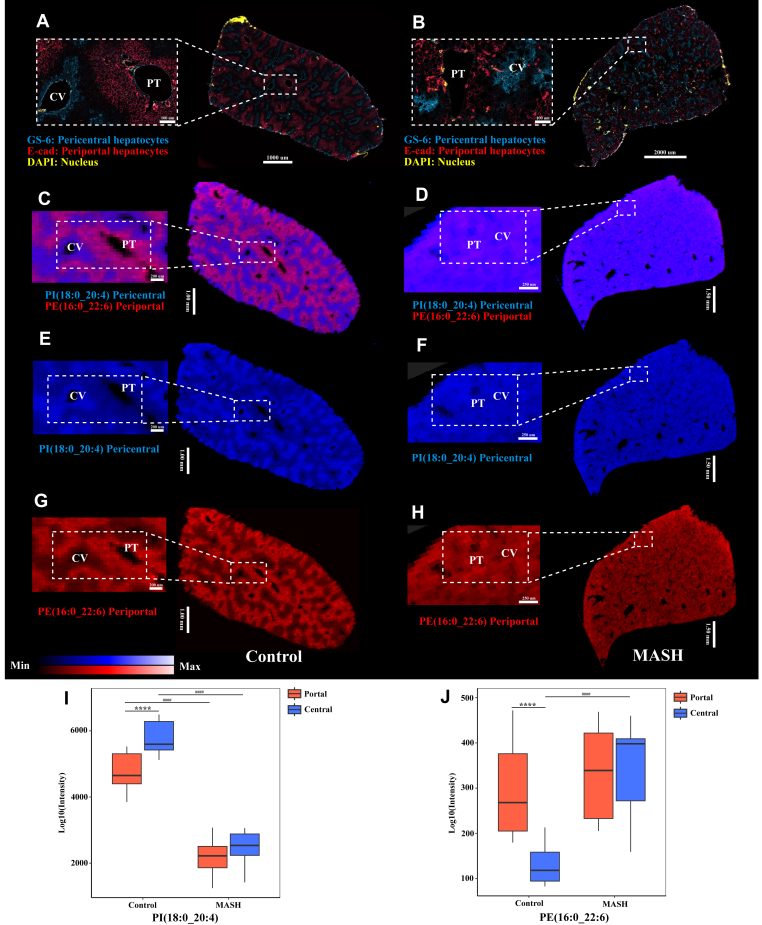
Fig. 5.
The zonation patterns observed in control and MASH livers by double-immunofluorescence staining and molecular imaging with DESI. Double-immunofluorescence staining shows the proto-central axis and the liver zonation of control (A) and MASH (B) livers. GS-6, pericentral hepatocytes (blue); E-Cad, periportal hepatocytes (red); and DAPI (yellow). Red and blue overlay ion images from DESI-MSI: PI(18:0_20:4) located in the pericentral area (blue) and PE(16:0_22:6) predominantly presented in the periportal region (red) of control (C) and MASH (D) livers. Ion images displayed spatial distribution obtained from control and MASH mice show the predominantly localisation of PI(18:0_20:4) in the pericentral (E, control) and (F, MASH) and PE(16:0_22:6) in the periportal (G, control) and (H, MASH). CV, central vein; PT, Portal tried; GS-6, glutamine synthetase; E-Cad, E-cadherin. Box plots visualising the zone-specific alteration of PI(18:0_20:4) (I) and PE(16:0_22:6) (J) across the liver zonation in control and MASH livers. The box plot data for PE(16:0_22:6) presented in the Figure are the same as those in Fig. 4A. This reuse is intended to highlight the lipid's specific localisation and changes in the MASH group's pericentral areas. ####P-value < 0.0001 the MASH compared with the control, ∗∗∗∗P-value < 0.0001 the pericentral areas of each group compared with the periportal areas.